
The Evolution of Analytics
Data and analytics have undergone a significant transformation in recent years. Advanced tools once reserved for experts are now accessible to everyone thanks to machine learning.
1. Traditional Analytics: Traditional analytics is usually driven by the IT department or specialists with the expertise and skills to handle complex data and tools. Users cannot explore and analyze data independently and rely on specialists to perform most tasks. The tools used for traditional analytics are advanced and designed for data and analytics professionals. Traditional analytics also produces large-scale reports covering various topics and metrics.
2. Self-Service Analytics: One of the trends in analytics is the emergence of business-led analytics, where business users take a more active role in driving the analytics process. This requires user-friendly tools that enable users to conduct analytics tasks independently without relying on IT or data experts. The goal is to empower users to generate insights and make data-driven decisions.
3. Augmented Analytics: Augmented analytics is a new paradigm that combines AI and machine learning-led technologies with complete user independence. Users can leverage AI tools and guided workflows to drive the analytics process without relying on experts or IT. Augmented analytics enables fast, deep, and previously hidden insights that can transform business decisions and outcomes.
Key Components of Augmented Analytics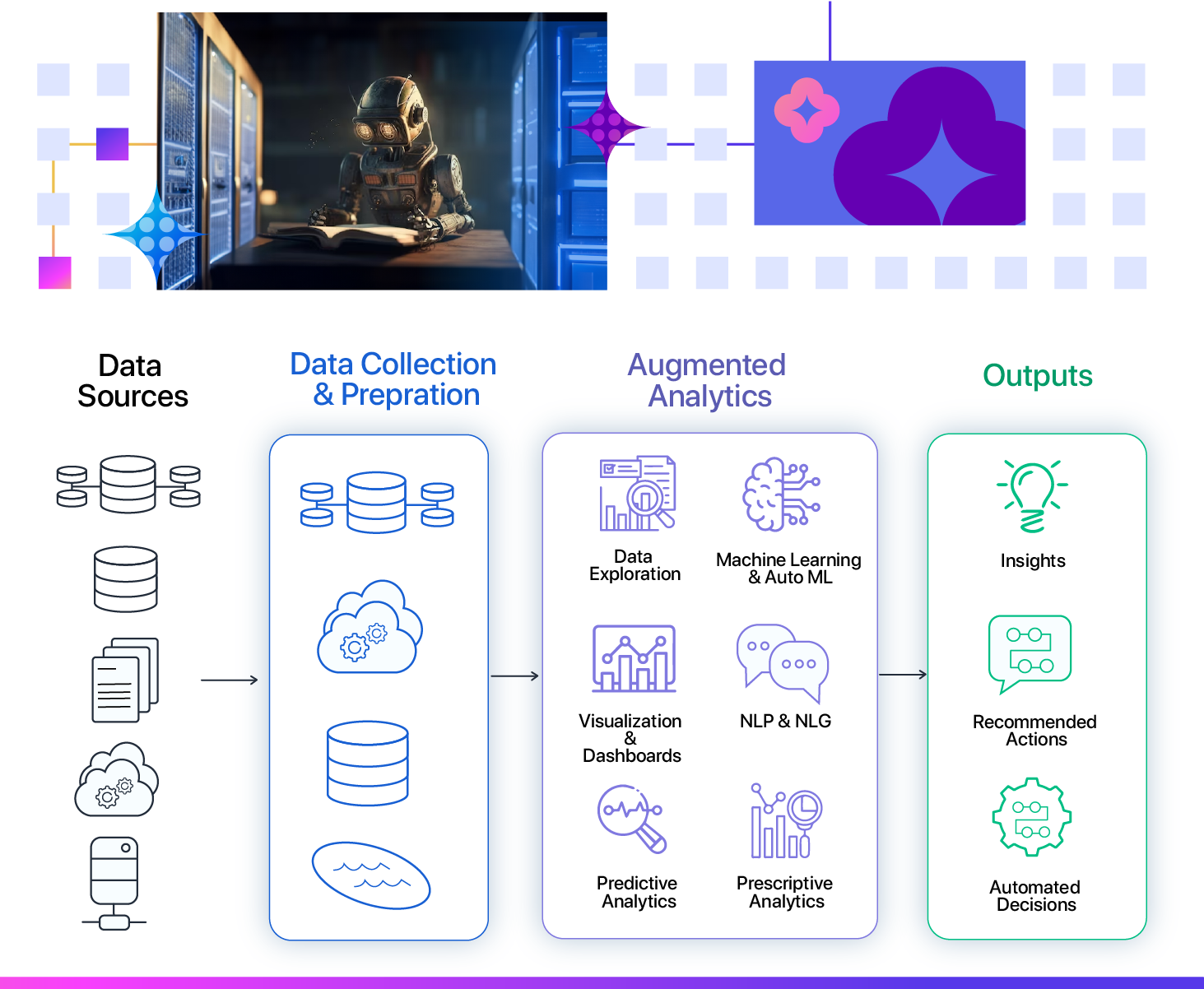
The cloud-based platform of augmented analytics, also known as AI analytics, effectively merges data and analytics. By streamlining data management and empowering various types of analytics, it offers a simplified approach to data analysis.
-
Data Collection and Preparation: AI automates data collection, cleaning, and integration from diverse sources. It handles big data sets, identifies potential errors, and recognizes specific attributes. The automated nature of AI ensures rapid and accurate data processing, improving overall efficiency. It minimizes manual effort for routine tasks, allowing data professionals to focus on more complex aspects of analysis and decision-making.
-
Data Exploration and Visualization: The incorporation of sophisticated algorithms for analysis and visualization greatly enhances the process of data discovery, mining, and representation. Utilizing Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques such as clustering and anomaly detection allows for the identification of hidden patterns and anomalies within the data. AI-driven visualization tools enhance data exploration by providing interactive and user-friendly visual displays. These tools allow users to understand data and extract actionable insights comprehensively.
-
Machine Learning and Statistical Analysis: Machine learning (ML) constructs models by analyzing historical data in order to forecast patterns and make informed choices with limited human involvement. These models are used in AI data analytics applications, such as recommendation systems and search-based analytics in natural language processing. The best-augmented analytics tools are equipped with AutoML capabilities, enabling custom ML models to be created without requiring extensive training.
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Natural Language Generation (NLG): NLP and NLG are crucial tools for data analysis. They help computers and humans communicate effectively, extract critical information from large amounts of text-based data, and perform sentiment analysis to detect emotional tone. With NLG, analytics tools can provide easy-to-understand responses and generate reports in your language. This automated process enhances efficiency and conserves valuable resources, enabling compliance teams to efficiently extract crucial information from organized data. Sophisticated natural language generation (NLG) tools equipped with machine learning capabilities have the ability to provide comprehensive responses to intricate inquiries.
-
Predictive Analytics: AI allows for the development precise prediction models that handle complex data, nonlinear relationships, and intricate features. Algorithms like ensemble learning and deep neural networks improve the accuracy and reliability of these models even further.
-
Prescriptive Analytics: Prescriptive analytics uses advanced techniques to analyze data and provide specific recommendations for the optimal action or strategy to take in the future. It helps companies optimize inventory levels, pricing strategies, marketing campaigns, or customer service. It can also suggest the best actions in other applications, such as CRM or ERP software, based on data and rules. It answers the question, "What is the best course of action?" using mathematical models, algorithms, and simulations.
1. Agility: AI-powered augmentation streamlines the search space, presents relevant data, and suggests productive analysis paths. This agility lets users answer data questions faster, freeing time for more strategic tasks.The benefit of augmented analytics and augmented analytics tools
2. Accuracy: Machine learning and AI technologies ensure accuracy by efficiently handling repetitive tasks. Augmented analytics provides a comprehensive view, reducing the risk of confirmation bias and enabling users to make informed decisions based on thorough analysis.
3. Efficiency: Augmented analytics leverages machine learning and AI to automate specialized, repetitive tasks in data preparation, discovery, and statistical analyses. This automation enhances efficiency, saving users time and energy.
4. Confidence: Augmented analytics tools are designed to be user-friendly, making data analysis more approachable for a broader audience. Integration into business workflows allows seamless exploration of specific questions. The context-aware nature of augmented analytics instills confidence in conclusions, leveraging users' industry expertise
Challenges of augmented analytics tools
Adopting Augmented Analytics is a significant step in transforming the data and analytics market, offering the potential for a competitive advantage. However, several challenges and resistances may impede its integration. Key challenges include:
Adoption Challenges
-
Outcome Expectations: Organizations often expect quick and favorable results from augmented analytics. However, technology has its lifecycle, utilizing AI computation, analytics, and automation techniques. Maturation and improvement in analysis and outcomes require time.
-
"Black Box" Image: Augmented analytics is perceived as a "black box," lacking transparency in decision-making. Trust in recommendations and insights is hindered without clear explanations, impacting user confidence.
-
Dependency on Legacy Platforms: Organizations may face challenges due to a reliance on legacy analytics platforms, acting as barriers to adopting augmented analytics.
-
Job Security Concerns: Automation in analytical operations raises concerns about job security as traditional workloads and processes undergo significant revamping.
-
Resistance from Business Leaders: Business leaders may resist adapting to changing scenarios, preferring intuition and traditional decision-making practices over augmented analytics.
-
Misconception of Linear Progression: There's a misconception that augmented analytics maturity follows a linear, progressive path, implemented once a robust foundation is established.
Governance Challenges
-
Need for AI Governance: There's a critical need to emphasize AI and analytics governance and collaboration between analysts and data scientists to support the growing presence of citizen data scientists within business units.
-
Governance for Analytic Content: Leaders must establish rules to govern analytic content and insights generated by augmented analytics. This ensures accuracy and validity and manages bias levels in findings and recommendations.
Use cases for augmented analytics
| Different Sector | Benefits |
|---|---|
|
Finance |
Financial Forecasting: Augmented analytics leverages historical data and external factors for forecasting revenue, expenses, cash flow, and profitability. It facilitates scenario and what-if analysis for evaluating diverse outcomes and risks. Financial Reporting: Augmented analytics generates interactive, dynamic reports and dashboards to concisely present financial performance and key metrics. It also offers natural language explanations and narratives. Financial Risk Management: Augmented analytics identifies and monitors financial risks like credit, market, liquidity, and operational risks. It provides alerts and suggestions for mitigating or preventing potential losses. |
|
HR |
|
|
Retail |
|
|
Health care |
|
|
Sales and Marketing |
|
|
Manufacturing |
|
Conclusion
The functionalities of augmented analytics have transformative applications across all sectors, streamlining business operations and improving access to valuable data. Successful adoption requires a holistic approach, addressing challenges in strategy, people, process, data, and technology components.
Read more about Top Real-Time Analytics Use Cases
Learn more about Real-time Analytics: Transforming Data into Instant Insights
Explore more about Augmented Analytics in Healthcare and its Use Cases




