What is Apache Sqoop?
Many still wonder what Apache Sqoop is, its architecture, features, uses, and how it relates to big data. In this Sqoop write-up, we will discuss everything and its requirements. Let’s get started! Apache Sqoop is a big data tool for transferring data between Hadoop and relational database servers.
It transfers data from RDBMS (relational database management system), such as MySQL and Oracle, to HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System). It can also transform data in Hadoop MapReduce and then export it into RDBMS. It is a data collection and ingestion tool that import and export data between RDBMS and HDFS.
SQOOP = SQL + HADOOP
Why do we need it?
It is primarily used for bulk data transfer to and from relational databases or mainframes. It can import from entire tables or allow the user to specify predicates to restrict data selection. You can write directly to HDFS as Sequence files or Avro. It can take data directly into Hive or Hbase with proper command line arguments. Finally, you can export data back to relational databases using Sqoop in Big Data.
A typical workflow with Big Data Hadoop Sqoop is where data is brought in Hive, so intermediate processing and transformation tasks can be done on Apache Hadoop. Once processing is done, data can be exported back to a database. This is one of many ways to perform "data warehouse offloading," where Hadoop is used for ETL purposes.
Before choosing Sqoop for your business, it is important to check structures, methods, and informational indexes in your big data platforms to obtain the best performance. Ask one of our Testing Experts for advice
What are the key features of it?
-
Parallel Import/Export: The Sqoop Big Data Tool uses the YARN framework to import and export data. This provides fault tolerance in addition to parallelism.
-
Import Results of SQL Query: Big Data Hadoop Sqoop allows us to import the result returned from an SQL query into HDFS
-
Connectors for All Major RDBMS Databases: It provides connectors for multiple Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) databases such as MySQL and MS SQL Server
-
Offers Full and Incremental Load: It can load the whole table or parts of the table with a single command, supporting both full and incremental load.
Sqoop Import
It imports every single table from RDBMS to HDFS. Each row within a table is treated as a single record in HDFS. All records are then stored as text data in text files or as binary data in Avro and Sequence files.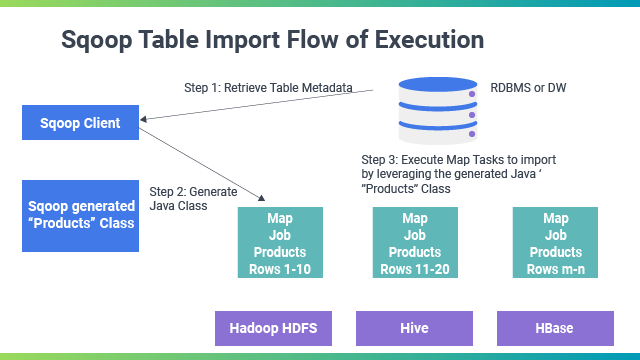
Sqoop Export
Its tool exports files from HDFS back to an RDBMS. All the files given as input to it contain records, which are called rows in the table. Later, those are read and parsed into a set of documents and delimited with a user-specified delimiter.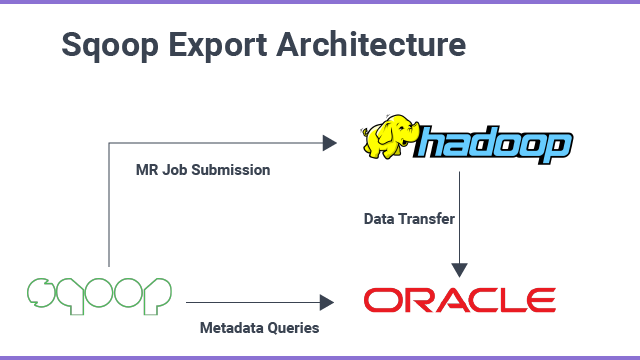
Where can we use it?
Relational database systems interact with business applications and are one of the most significant and largest sources in the modern world. Different processing frameworks like MapReduce, Hive, HBase, Cassandra, Pig, etc. in Hadoop and storage frameworks like HDFS can benefit distributed computing and storage.
Data must be transferred among database systems and the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) to store and analyze it from relational databases. Here, Sqoop in Big Data comes into the picture. It acts like a middleman/layer between Hadoop and relational database systems. One can import and export data between relational database systems and Hadoop and its ecosystems directly using it.
Sqoop in Big Data provides a command-line interface to the end-users. It can also be accessed through Java APIs. It parses the user's command, and it launches Hadoop Map only to import or export data because the Reduce phase is only required when aggregations are required. It just imports and exports the information; it does not do aggregations. It parses the arguments given in the command line and prepares the Map job.
A map job launching multiple mappers depends on the number defined by the user in the command line. During Sqoop import, each mapper task is assigned to import part of the data based on the command line. Data is distributed equally among the mappers to achieve high performance. After that, each mapper creates a connection with the database using JDBC and then imports the part of the data it provides. Then, it is written into the HDFS, Hive, or Apache HBase according to the option provided in the command line.
What is the difference between Apache Flume and Apache SQOOP?
Apache Sqoop and Apache Flume work with different kinds of data sources. Flume functions well in streaming data sources generated continuously in a Hadoop environment, such as log files from multiple servers. On the other hand, Apache Sqoop is designed to work well with any relational database system with JDBC connectivity.
Sqoop can also import data from NoSQL databases like MongoDB or Cassandra, allowing direct data transfer, Hive, or HDFS. A table must be created to transfer data to Hive using the Apache Sqoop tool, and the schema must be taken from the original database. In Apache Flume, data loading is events that do not drive event-driven, whereas in Apache Sqoop, data load. 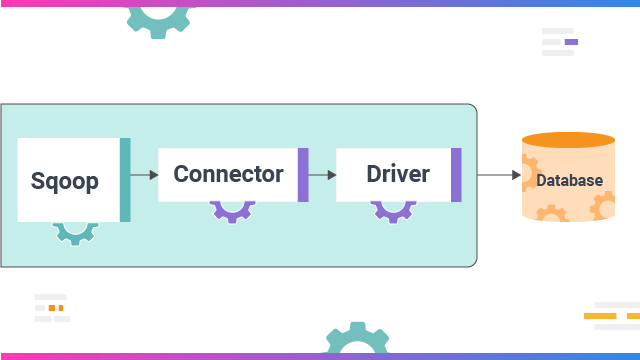 Flume is better when moving bulk streaming data from sources like JMS or the Spooling directory. In contrast, it is an ideal choice. If the data is saved in databases like Teradata, Oracle, MySQL Server, Postgres, or any other JDBC-compatible database, it is best to use it. In Apache Flume, data flows from HDFS through multiple channels.
Flume is better when moving bulk streaming data from sources like JMS or the Spooling directory. In contrast, it is an ideal choice. If the data is saved in databases like Teradata, Oracle, MySQL Server, Postgres, or any other JDBC-compatible database, it is best to use it. In Apache Flume, data flows from HDFS through multiple channels.
Apache Flume, Big Data Ingestion has agent-based architecture, i.e., the code written in the flume is an agent responsible for fetching data. In contrast, its architecture is based on the connectors. The connectors in Sqoop know how to connect with the various data sources and fetch data accordingly. 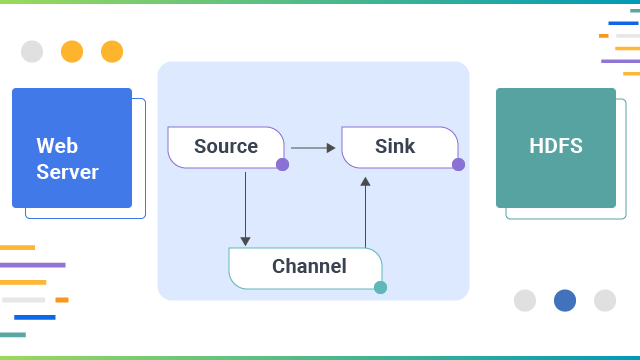 Sqoop and Flume cannot be used to achieve the same tasks as they are developed specifically to serve different purposes. Apache Flume agents are developed to fetch streaming data like tweets from Twitter or log files from the web server, whereas its connectors are designed to work only with structured data sources and fetch data from them.
Sqoop and Flume cannot be used to achieve the same tasks as they are developed specifically to serve different purposes. Apache Flume agents are developed to fetch streaming data like tweets from Twitter or log files from the web server, whereas its connectors are designed to work only with structured data sources and fetch data from them.
It is used for parallel data transfers and imports as it copies data quickly. In contrast, Apache Flume collects and aggregates data as it is distributed, the true nature, and highly available backup routes.
| Features | Apache Sqoop | Apache Flume |
| Functionality | Works well for Streaming data sources generated continuously in a Hadoop environment | Any relational database system with JDBC connectivity. |
Architecture |
Connector-Based Architecture | Agent-Based Architecture |
| Driven Events | Not Event Driven | Completely Event-Driven. |
| Where to use | Parallel data transfers and data imports as it copies data quickly | Pull Data from different sources to analyze the patterns, perform sentiment analysis, etc |
Next Steps with Big Data Sqoop
Talk to our experts about implementing compound AI system, How Industries and different departments use Agentic Workflows and Decision Intelligence to Become Decision Centric. Utilizes AI to automate and optimize IT support and operations, improving efficiency and responsiveness.
.webp?width=1921&height=622&name=usecase-banner%20(1).webp)


