Pros of Cloud-native Autonomous SOCs
-
Threat Identification and Response in Less Time
Automation lessens the time needed to detect and contain breaches, thus limiting their detrimental impact on the company.
-
Reduced Human Workload
Tasks, including log analysis and alert sorting, are time-consuming and can be eliminated by an autonomic system so SOC analysts can engage in higher tasks such as hunting for threats and planning.
-
Improved Cost-efficiency
Organizations prevent spending on hardware input and decrease numerous operational expenses through cloud structure and automation.
-
Scalability to Meet Business Needs
The cloud-native method helps SOCs to get thorough flexibility in bandwidth so that, during rush hour, it could easily accommodate the additional workload while, in low demanding time, allowing itself to shrink down.
-
Broadened Exposure in Each Cloud Sector
Traditional SOCs, on the other hand, are cloud-native and designed to offer visibility for multi-cloud and hybrid environments to facilitate cohesive security orchestration.
Challenges in Implementing a Cloud-native Autonomous SOC 
-
Complexity of Cloud Environments
Organizations normally have complex, hybrid, or multi-cloud setups. This can make ensuring seamless integration across diverse platforms challenging.
-
Data Overload
The vast amount of security data generated in cloud environments can be overwhelming. Misconfiguration models can lead to undetected threats or an excess of false positives.
-
Skill Gaps
Managing and optimizing an autonomous SOC requires cloud security and automation capability, skills in high demand but scarce.
-
Initial Implementation Costs
Moving to a cloud-native SOC necessitates a considerable upfront investment in tools and training of existing processes.
-
Regulatory Challenges
Cross-border data flows in cloud environments may complicate compliance with regulations, requiring careful attention to data governance.
The solutions that are enabling Cloud-native Autonomous SOCs
-
Autonomous SOCs also rely on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning AI/ML models for predictive analytical outcomes, Anomaly detection, and an automated response to threats.
-
Big Data Analytics The effectiveness of handling large volumes of data in real-time provides useful information to security teams.
-
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) is a set of tools for scanning cloud configurations for compliance issues and security concerns and then “fixing” them.
-
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Current generation cloud SIEM solutions process security logs to detect threats.
-
Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platforms combine with SOC tools to automate processes such as incident management and threat management.
-
Security Identity and Access Management (IAM) Strong IAM solutions implement zero-trust principles, so nobody but an authenticated user can access cloud resources.
Process to Design a Cloud-native Autonomous SOC
-
Assess Organizational Needs First, ensure you fully understand your organization’s cloud infrastructure, including its strengths, weaknesses, and compliance.
-
A cloud-native security framework should be embraced. Choose a framework that supports your cloud providers and plugs well into native tools.
-
Opt for AI and automation. Learn the best techniques for threat detection, response automation and the use of AI and machine learning.
-
Support ongoing control by implementing real-time monitoring technology to promote the overall view of the cloud resources and structures.
-
Train Your Team Shifting to cloud security, artificial intelligence, and automation will help you train your SOC team to monitor the autonomous SOC adequately.
-
Policies should be periodically reviewed because threats may appear, and changes in the legal framework may occur.
Popular Cloud-native Autonomous SOCs Cases
Live Ransomware ThwartingReal-time threat hunting in a cloud-native SOC identifies when files are encrypted and the infrastructure shuts down the infected computers.Information LifecycleThe SOC guarantees that an organization's data is stored and processed only in permitted areas under GDPR; it also prepares compliance reports.Advanced Persistent Threat (APT)The SOC identifies long-term reconnaissance or lateral movements characteristic of APT Detection. Using AI, the SOC triggers anti-APT measures.DevSecOps IntegrationA financial institution brings the SOC with CI/CD pipelines to scan source code for vulnerabilities before the app release.
Examples of pioneered Cloud-native Autonomous SOC Solutions
-
Microsoft Sentinel: A cloud SIEM and SOAR solution, Microsoft Sentinel employs AI to uncover threats in hybrid and multi-cloud deployment modes.
-
Google Chronicle: It comes with real-time threat detection and analysis that Google’s cloud service can enjoy.
-
AWS Security Hub: It is a fully managed tool designed to collaborate with other AWS solutions to discover threats and conduct security assessments for applications running in the AWS environment.
-
IBM Cloud Pak for Security: This solution integrates various security information sources. Its work is based on AI and AV features that provide unified threat intelligence and response.
The Cloud-native Autonomous SOC is the new generation of infosec as it adapts AI and automation to handle modern cloud issues. These SOCs are designed cloud-native to harness the power of autonomy while leveraging the flexibility of a cloud-native design to combat more complex threats with fewer costs and systems complexity. Today, clouds are becoming increasingly commonplace. More organizations are shifting to it, therefore making the Cloud-native Autonomous SOC a necessity. Using modern trends and proper planning of cybersecurity measures, companies can protect their data and IT systems, follow regulations and have strong cybersecurity protection in the modern threat environment.
.webp?width=1921&height=622&name=usecase-banner%20(1).webp)
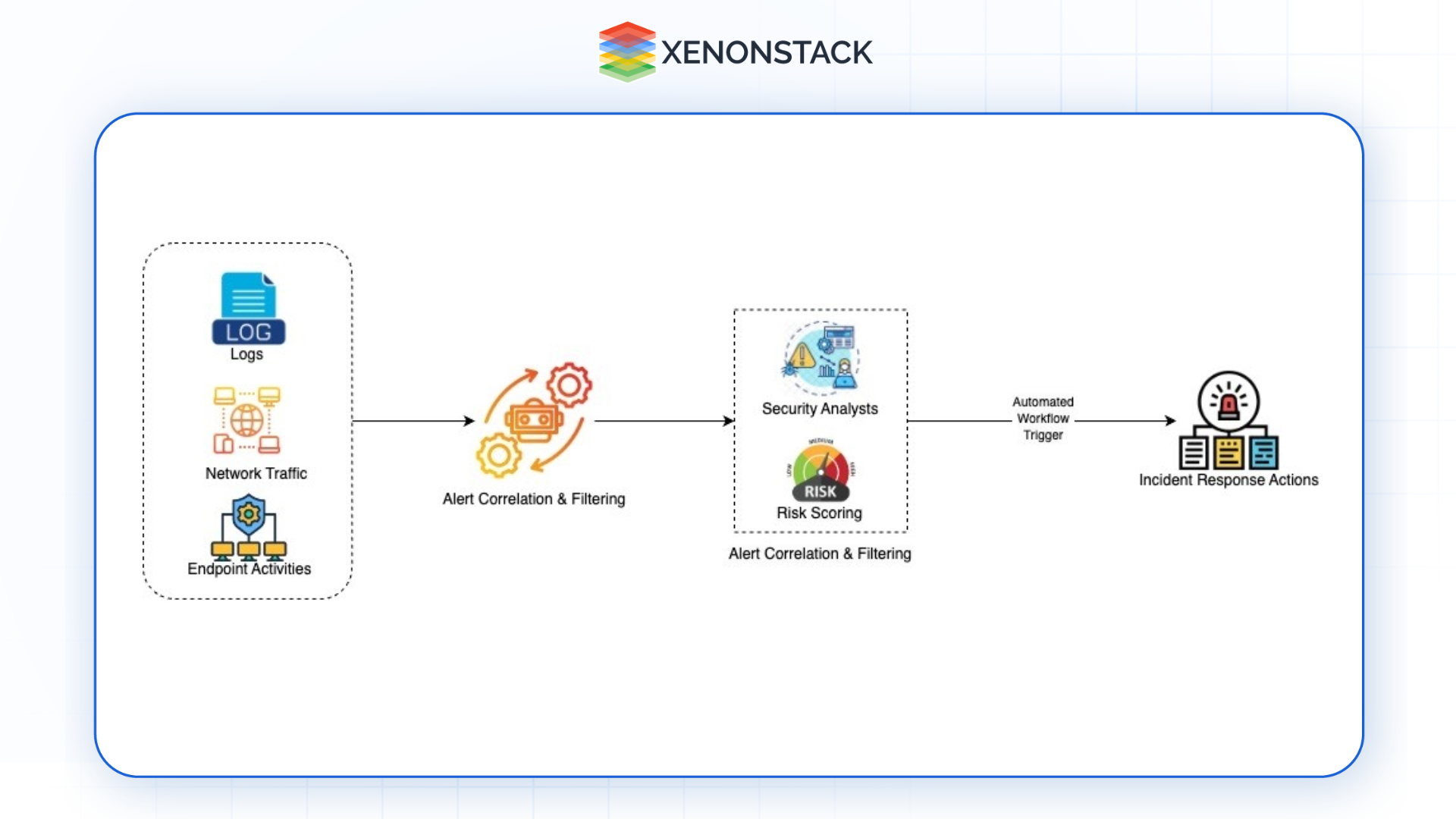
 Figure 2: Some benefits of cloud-native architecture
Figure 2: Some benefits of cloud-native architecture 



