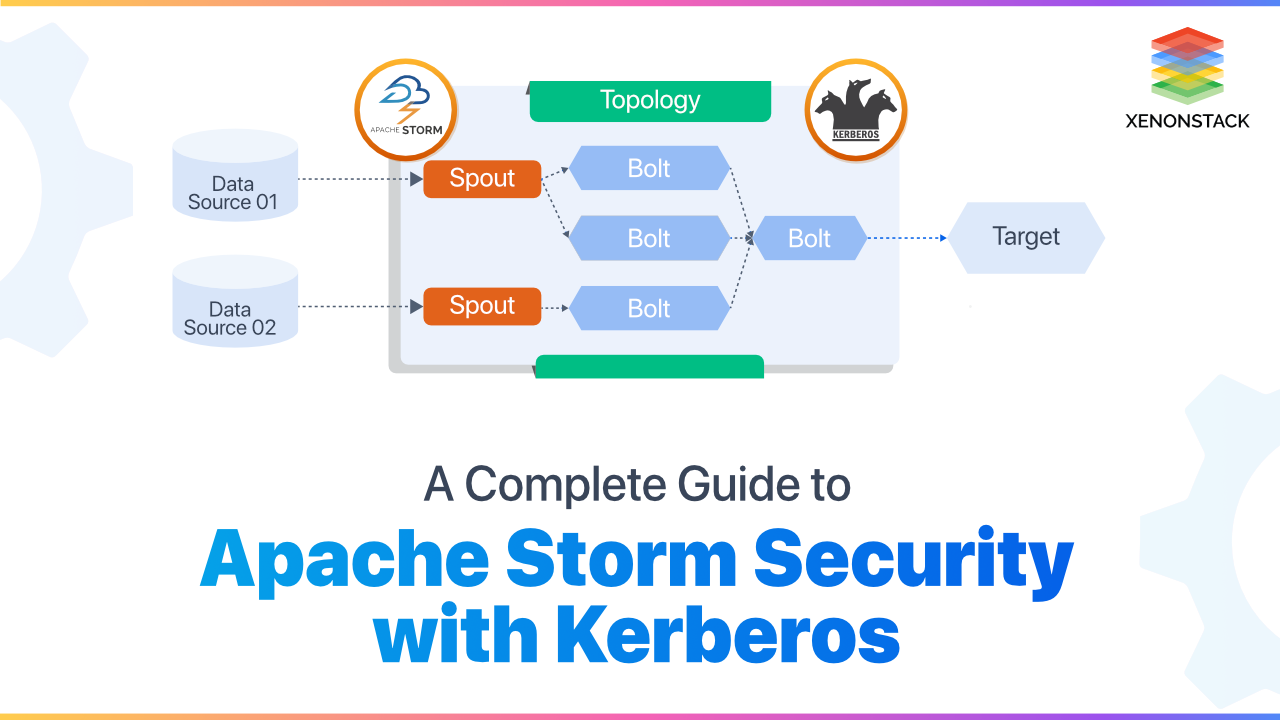
Introduction to Security Operation Center (SOC)
The cyber threat landscape is growing and rapidly changing, and preventing possible cyberattacks necessitates constant monitoring and response. The longer a cybersecurity incident goes unresolved, the greater the risk of damage and expense to the organization. The Security Operations Center of an organization is responsible for dealing with these risks. It should be able to monitor cyber threats 24 hours a day, seven days a week, and respond to incidents quickly.
What is Security Operation Center?
A security operations center is a structure that contains an information security team that is in charge of continuously monitoring and assessing an organization's security posture.
The team uses a combination of a set of processes to detect, evaluate, and respond to cybersecurity problems. The team collaborates with organizational incident response teams to ensure that security vulnerabilities are addressed as soon as they are discovered. It monitors and analyze networks, servers, endpoints, databases, apps, websites, and other systems, which check for unusual behavior that could indicate a security incident or compromise. The security operations center is responsible for properly identifying, analyzing, defending, investigating, and reporting potential security threats.
The security measures at the application level that secures the data or the code from being stolen. Taken From Article, Application Security Checklist and Strategy
Responsibilities of Security Operation Center (SOC)
The Security Operations Center leads organization incident response and pushes continuing security enhancements to defend the organization from cyber threats. A well-functioning SOC will give the following benefits by using a complicated combination of the proper technologies and the right people to monitor and manage the entire network.
- Identify Assets: SOC teams gain in-depth knowledge of network hardware and software to detect threats and weaknesses early.
- Proactive Monitoring: Continuous monitoring for malicious activity to prevent potential damage before it escalates.
- Rank Alerts by Severity: Analysts assess and prioritize threats, ensuring the most critical issues are addressed first.
- Incident Recovery: Involves data recovery, system reconfiguration, updates, and backups to restore normal operations post-incident.
- Compliance Management: Ensures adherence to regulatory standards and internal policies; often handled by a dedicated compliance officer.
- Behavioral Monitoring: 24/7 monitoring to detect abnormal activities using behavioral models to reduce false positives and ensure prompt detection.
- Ongoing Security Enhancements: Constantly improving defenses by analyzing incidents and applying lessons learned to strengthen security measures.
Role of Compliance in SOC Operations
- Ensuring Regulatory Adherence - Compliance with standards like NIST and ISO 27001 is crucial for SOCs to align with industry regulations and create effective security policies.
- Monitoring and Reporting - SOCs must monitor activities and generate reports to ensure compliance, particularly in incident management and cybersecurity responses.
- Supporting the Zero Trust Model - SOCs adopt the Zero Trust Security Model to enforce strict access controls and minimize unauthorized data access, helping meet regulatory requirements.
- Compliance Audits - Regular audits ensure SOCs follow security policies, helping organizations avoid penalties and reputational damage.
- Training and Education - SOCs train teams on compliance requirements, ensuring they follow risk assessment frameworks and meet industry standards.
Challenges Faced by SOCs
-
Increasing Cybersecurity Incidents - As organizations face an increasing volume of cybersecurity incidents, SOCs must implement continuous monitoring to detect and respond quickly to threats such as malware, ransomware, and data breaches.
-
Managing Threat Intelligence - Effective threat intelligence is critical to SOCs for identifying potential risks before they escalate. With constantly evolving cyber threats, SOCs need to stay ahead by integrating AI-driven insights and data from multiple sources.
-
Skills Shortage - A major challenge is the shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals, which makes it harder for organizations to maintain effective SOC operations. This often leads to delays in incident management and a slower response to potential threats.
-
Vulnerability Management - SOCs need to continuously monitor systems for vulnerabilities. Without proper tools and automated processes, managing and remediating vulnerabilities can be time-consuming, which may expose the organization to risks.
-
Data Breach Response - Data breach response is a top priority for SOCs. In the event of a breach, SOCs must quickly identify the source, contain the attack, and begin the recovery process, which requires a coordinated, well-executed strategy.
Types of Security Operations Centers (SOC)
The following are numerous security operations center models that a business can employ and determine which job responsibilities are included on the team.
- Dedicated (Self-Managed): In-house team managing an on-site facility.
- Distributed SOC: In-house team collaborates with a third-party MSSP for co-managed security.
- Managed SOC: Full security services provided by MSSPs or MDR partners.
- Command SOC: Focuses on threat intelligence and supports other SOCs.
- Fusion Center: Integrates security operations with IT, DevOps, and other enterprise teams.
- Multifunction SOC: Expands its role to cover IT management, including network operations.
- Virtual SOC: No dedicated facility; relies on in-house or cloud-based teams for operations.
- SOCaaS: Cloud-based, subscription-driven service outsourcing some SOC functions.
A cloud-native development methodology that enables developers to create and execute apps without worrying about managing servers. Taken From Article, What is Serverless Security?
Benefits of a Security Operations Center
Following are the benefits of the SOC:
- Improved incident response times and practices.
- Decreased gaps between the time of compromise and mean time to detect (MTTD).
-
Continuous monitoring and analysis for suspicious activities.
- Consolidated software and hardware assets for a more holistic security strategy.
- Customers and workers feel more comfortable sharing sensitive information.
- Increased transparency and control over security activities
To explore how Xenonstack's Cyber Security services can help strengthen your organization's security posture, visit our comprehensive solutions page here.
Guidelines for Effective Deployment of SOC Tools
Using the right tools is essential for a Security Operations Center (SOC) to be able to effectively detect and respond to security incidents. Below are some best practices for using SOC tools:
- Regularly Update and Patch Tools: These tools should be regularly updated and patched to ensure that they are protected against the latest threats.
- Properly Configure Tools: Security operation center tools should be properly configured to ensure that they are able to detect and respond to the types of threats that are relevant to the organization.
- Regularly Test Tools: SOC tools should be regularly tested to ensure that they are functioning properly and that they are able to detect and respond to simulated security incidents.
- Integrate Tools with Other Systems: SOC tools should be integrated with other systems, such as incident response platforms and threat intelligence platforms, to ensure that they are able to effectively share information and respond to security incidents.
- Use Multiple Tools: SOCs should use multiple tools to provide a layered approach to security. This can help to ensure that threats are detected and responded to even if one tool is bypassed.
- Monitor Tools Performance: SOC should monitor the performance of the tools to ensure that they are running efficiently and effectively.
- Establish a Baseline: Establishing a baseline of normal activity can help to identify abnormal activity that may indicate a security incident.
- Use Automation: Automation can help SOC teams to quickly and efficiently respond to security incidents and manage large amounts of data.
By following these best practices, SOCs can effectively use tools to detect and respond to security incidents, improve overall security posture, and comply with industry regulations and standards.
SRE team is responsible for resolving incidents, automating operational tasks, using the software to manage systems. Taken From Article, Managed SRE Challenges and Solutions
Best Practices for Security Operation Center Implementation
Following are the best practices of the Security Operations Center:
Risk Assessment
Formal risk assessment procedures are used by the leaders to identify gaps in detection and response coverage and to influence future investments.
Data Collection and Aggregation
Security operations centers that are best in class use cutting-edge technologies to consolidate and analyze data from across the enterprise effectively.
Prioritize
Even the largest teams might be overwhelmed by the volume of security data and alarms. To avoid ignoring critical threats, defined mechanisms for prioritizing and triaging incident response are necessary.
Using Playbooks
Playbooks are operational procedures that provide structure and step-by-step instructions for common attack scenarios to analysts. They improve response time and investigative quality.
Automation
To improve response times and free up analysts for critical tasks, the security operations center automates data collection and incident response. With autonomous operations, SOCs can independently analyze threats and respond. They also monitor cybersecurity effectiveness and ensure compliance. This version is concise while still conveying the essential points.
Autonomous operations and automation are crucial for SOCs, enabling faster threat analysis, response, and ensuring continuous monitoring and compliance.
What are the Essential Tools for SOC?
Here are the important tools that can help in setting up Security Operation Center in an Organisation
Snort
A snort is an open-source tool. It is a network Intrusion detection tool. It is a packet sniffer tool used for monitoring network traffic, carefully inspecting each packet for malicious payloads or suspicious anomalies. Users may compile Snort on most Linux operating systems (OSes) or Unix, making it a long-time leader among enterprise intrusion prevention and detection software. A Windows version is also available.
Vulnerability Scanner
It's crucial to have a vulnerability scanner to assess and check if any asset is running with serious flaws that could lead to a breach of security assault if you want to be proactive about security. The Vulnerability Scanner is a program that includes various updated scripts for detecting system and application vulnerabilities. Scans and patches systems on a regular basis, especially those that are external or connected to the Internet.
FTK
The acronym FTK stands for "forensic toolkit." It's a data research and imaging tool that's used to forensically capture data while also producing copies of the data without changing the original evidence file. Producing forensic photos of local hard discs, examining the content of images saved on the local workstation, and exporting files and directories from forensic files are all functionalities of the FTK Imager. The FTK imager also has an inbuilt validation feature that generates a hash report that can be used to validate the hash of the Evidence both before and after it is imaged.
Wireshark
Wireshark is a network packet analysis tool. It catches packets as they go via the network and converts them to a readable format. Color coding, filters, and other capabilities of Wireshark allow us to go deep into the packets and inspect them individually. It's an open-source tool for developing and learning protocols. The main goal is to raise awareness of how network packets are extracted and processed from the machine's runtime state, as well as the difficulties and complexities involved. It's a terrific way to learn about and explore the analysis.
Maltego
Maltego is a crucial instrument for large-scale data collection. Maltego can extract a lot of data from a single target or a group of targets, whether it's a domain, IP address, server, or something else entirely. It automates the procedure and helps you to present the data in a clear and understandable manner. Maltego is built on publicly available data, however, you must make sure that your data collection stays within the parameters you've specified. On Kali-Linux, Maltego is pre-installed and can be found in the information gathering section.
Future of Security Operations Centers
- Integration of MSSPs - SOCs will collaborate more with Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs), especially to support smaller businesses lacking internal resources.
- Automation of Security Operations - Automation tools will streamline SOC tasks, improving efficiency, reducing response times, and enhancing incident response capabilities.
- Adoption of Advanced Threat Intelligence - Advanced threat intelligence will help SOCs proactively detect attacks, improving early detection and response.
- Behavioral Analytics and AI - AI and behavioral analytics will enhance SOC capabilities by detecting patterns and anomalies, identifying both internal and external threats.
- Emphasis on Continuous Monitoring - The demand for continuous, real-time monitoring will increase as cyber threats become more sophisticated, requiring SOCs to scale operations and integrate advanced tools.
Summing Up SOC Tools and Strategies
Ultimately every firm attempts to protect its infrastructure from modern threats and reduce the likelihood of data breaches—but security structures, tactics, and entities are not 'one size fits all. Security operations centers are one of the most effective threat detection and prevention tools available to businesses. SOC with a hybrid design, which supports small and medium-sized businesses, were previously regarded to be solely appropriate for giant corporations. The effectiveness comes with a hybrid design, which supports small and medium-sized businesses, has debunked this assumption time and time again. Which choice is suitable for you will be determined by your security requirements and organizational structure.
Next Steps
Consult with our experts on implementing advanced AI systems within your Security Operation Center. Learn how industries and departments leverage Agentic Workflows and Decision Intelligence to become more decision-centric. Use AI to automate and optimize SOC operations, enhancing efficiency and responsiveness in IT support and security management.