What Are the Leading Agentic AI Frameworks?
In the emerging landscape of autonomous AI systems, several powerful frameworks are paving the way for machines that can think, plan, and act with minimal human oversight. These frameworks transform foundation models from passive responders into active problem-solvers capable of breaking down complex goals, utilizing tools, and executing multi-step plans. As AI transitions from generative to agentic capabilities, these specialized tools provide the crucial infrastructure that empowers models to function with increasing autonomy and effectiveness in real-world environments. 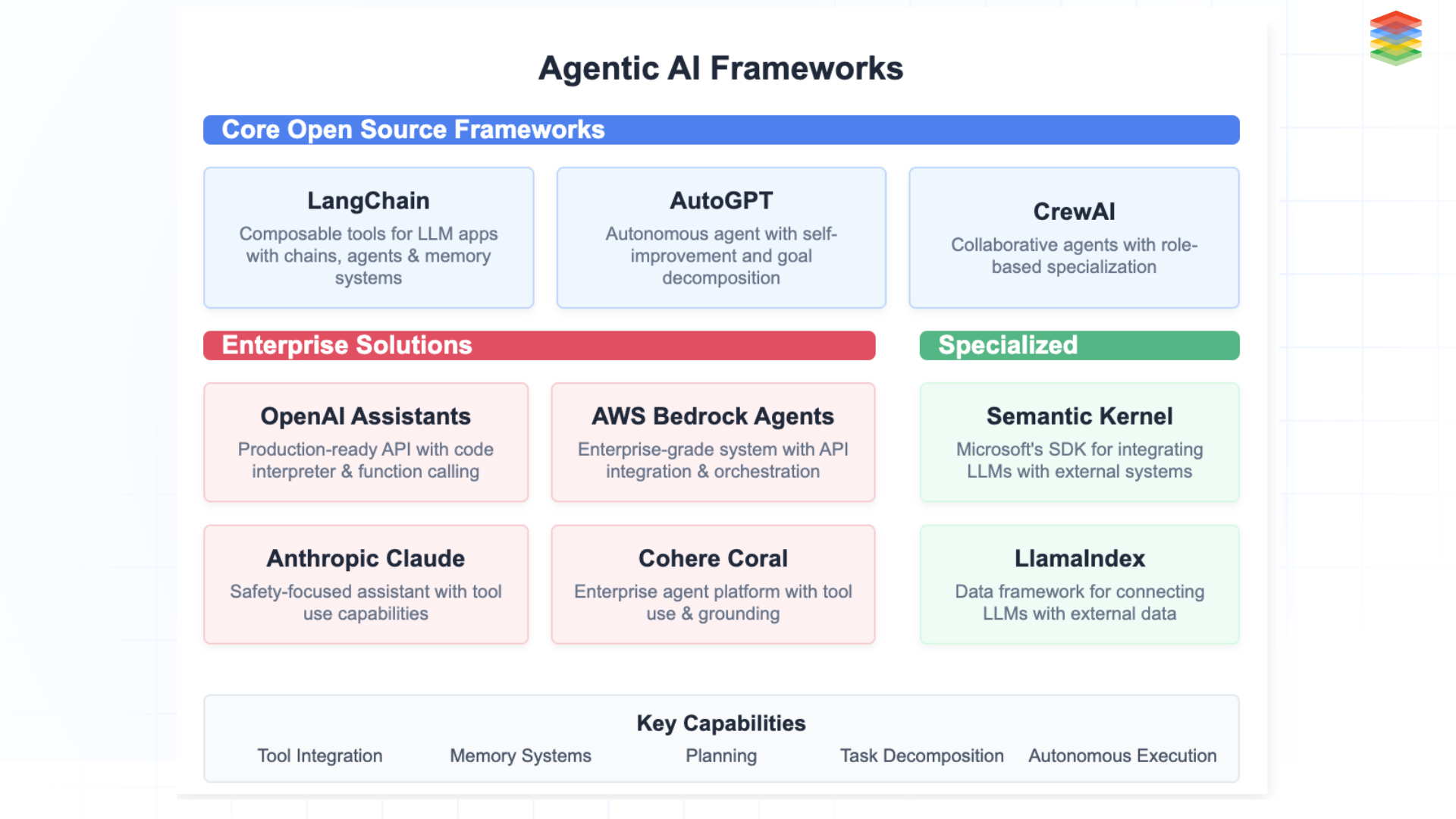
Fig 4: Agentic AI Framework
| Framework | Primary Use CaseKey | Differentiator | Maturity Level |
| LangChain | General-purpose agent development | Extensive tool ecosystem, production-ready | Mature |
| AutoGPT | Autonomous task execution | Self-directed goal pursuit | Experimental |
| CrewAI | Multi-agent collaboration | Role-based team coordination | Growing |
| Semantic Kernel | Enterprise integration | Microsoft ecosystem integration | Enterprise-ready |
| BabyAGI | Task management | Autonomous prioritization | Research-focused |
| AWS Bedrock Agents | Cloud-native deployment | Managed infrastructure, compliance | Production |
| OpenAI Assistants API | Developer platform | Native GPT integration | Production |
| Anthropic Claude Tools | Safety-critical applications | Constitutional AI guardrails | Production |
-
LangChain & AutoGPT: Pioneer frameworks enabling goal-oriented behaviour through modular tool integration and autonomous task execution, functioning as the "operating systems" for LLM-powered agents. These frameworks not only enable planning but also structure AI agentic workflows that scale across industries.
-
Specialised Agents: CrewAI for multi-agent collaboration, Semantic Kernel for symbolic-neural integration, and BabyAGI for autonomous task management—each addressing specific aspects of the agentic ecosystem.
-
Enterprise Solutions: AWS Bedrock Agents, OpenAI Assistants API, and Anthropic Claude Tools bring production-ready agentic capabilities to businesses with enhanced safety, scalability, and integration features.
How Do You Operationalise an Agentic AI Stack in Production?
Building effective agentic AI requires more than selecting a framework—it demands a systematic approach to training, testing, and deployment. Here's how to move from concept to production:
Foundation Model Selection & Tuning
Choose foundation models with strong reasoning capabilities, then optimise them specifically for agentic behaviour:
-
Fine-tune on expert demonstrations showing effective planning and tool use
-
Implement constitutional AI techniques for safety without sacrificing autonomy
-
Apply RLHF with feedback on complete agent trajectories, not just outputs.
Rigorous Testing Framework
Evaluate agents across multiple dimensions using:
-
Controlled environments with progressive complexity
-
Test suites measuring goal achievement, planning quality, and adaptability
-
Comparative benchmarks against human performance on identical tasks
-
AgentBench or similar standardized metrics for consistent evaluation
Specialized Optimization
Train agents using multi-objective optimization that balances:
-
Goal completion accuracy (primary objective)
-
Plan coherence and efficiency (minimizing unnecessary steps)
-
Tool selection appropriateness (using the right tool for each task)
-
Safety constraint adherence (avoiding risky actions)
Infrastructure Requirements
Enterprises need an infrastructure stack that supports real-time inference, sandboxed environments, and memory-optimized systems.
Deploy with robust infrastructure, including:
-
Low-latency inference systems for real-time decision-making
-
Sandboxed execution environments for tool usage
-
Comprehensive logging and monitoring of agent activities
-
Memory-optimized systems for maintaining context across interactions
Progressive Deployment Strategy
Follow a measured approach to production:
-
Begin with human oversight for all agent actions
-
Gradually increase autonomy for well-tested tasks.
-
Implement automatic escalation for low-confidence decisions.
-
Establish continuous feedback loops to improve performance.
What is the biggest challenge in operationalising Agentic AI?
Ensuring reliability, safety, and scalability while maintaining autonomy.
Addressing these operational aspects while maintaining appropriate safeguards can help organisations build reliable agentic AI systems that deliver real value. The key is treating agent development as a distinct discipline with its own unique requirements, metrics, and best practices.
What Are the Emerging Trends in the Agentic AI Development Stack 2025?
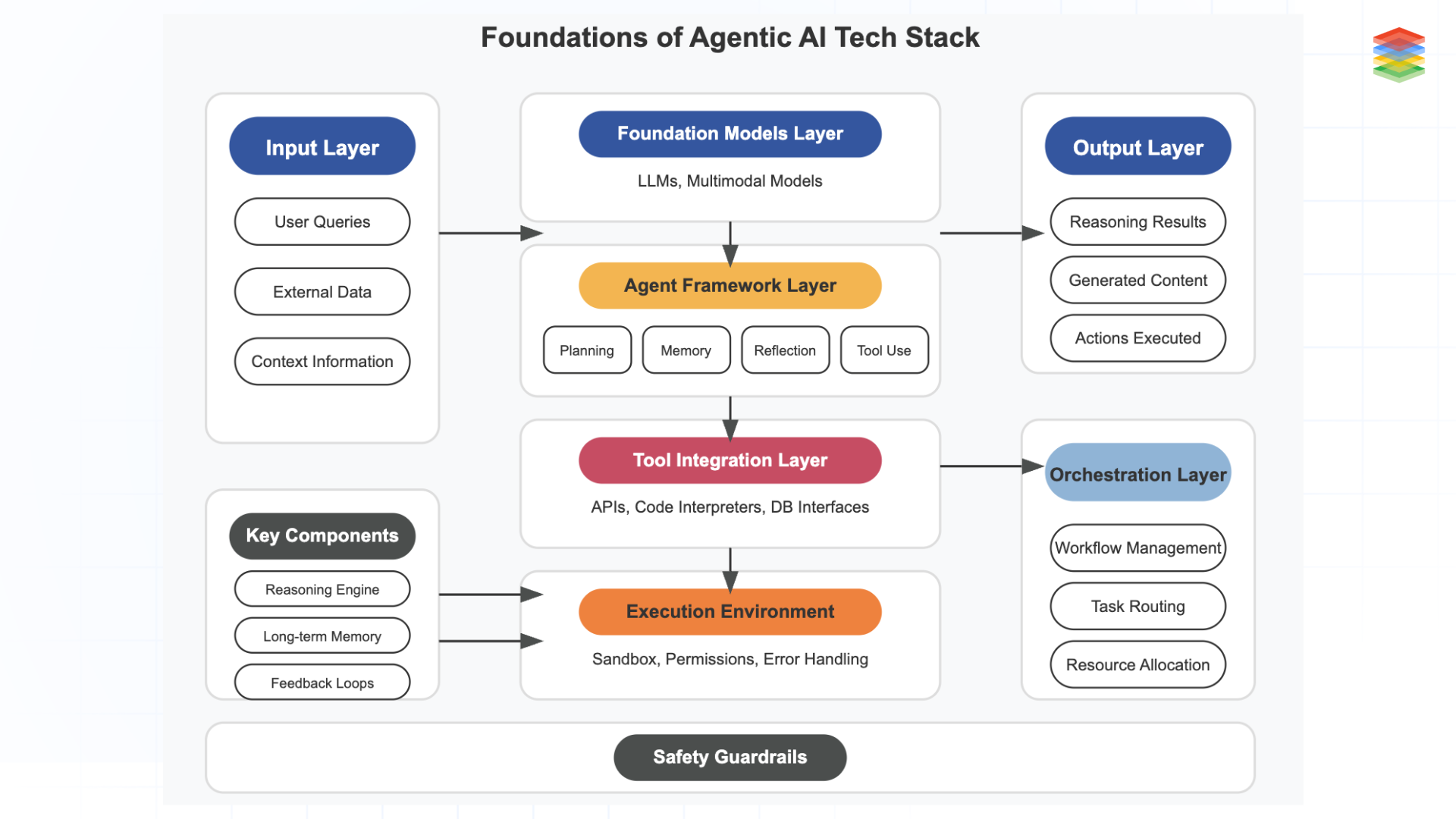
As we move into 2025, the agentic AI development stack has matured significantly, with specialised tools and platforms emerging to address the unique challenges of building autonomous AI systems. The ecosystem has evolved from experimental frameworks to production-ready solutions that enable organisations to build, deploy, and manage agentic AI at scale.
 Fig 5: Agentic AI Development Stack
Fig 5: Agentic AI Development Stack
What Are the Emerging Trends in Agentic AI Development for 2025?
As we enter 2025, the agentic AI development stack has matured from experimental to enterprise-ready. Organisations are now deploying autonomous systems at scale, utilising specialised components across the entire stack.
1. Foundation Models Built for Agency
-
Enhanced planning and reasoning capabilities
-
Built-in tool-use understanding
-
Longer context windows for complex tasks
-
Reduced hallucination for factual operations
2. Standardised Tool Integration
-
OpenTools Protocol for universal connectivity
-
Centralised security-verified tool registries
-
Simplified API authorization frameworks
3. Enterprise-Grade Agent Frameworks
-
Enterprise versions with SLAs and compliance features
-
Low-code agent creation platforms
-
Industry-specific solutions for finance, healthcare, and manufacturing
4. Reliability and Scale Infrastructure
-
Specialised cloud platforms for agent hosting
-
Advanced observability for tracking agent actions
-
Secure sandboxed execution environments.
5. Multi-Agent Orchestration
-
Coordination tools for specialised agent teams
-
Role-based architecture frameworks
-
Centralised monitoring dashboards
What Are the Critical Implementation Challenges?
Building an agentic AI stack unlocks powerful capabilities, including autonomous planning, tool use, and multi-agent collaboration. However, implementing such systems comes with several practical and technical hurdles.
-
Agent Coordination and orchestration are challenging in dynamic workflows because they involve managing agents' communication, sharing tasks, and avoiding conflicts.
-
Long-Term Planning & Goal Decomposition: Breaking abstract goals into concrete, adaptive steps remains a challenge for many systems.
-
Security & Safety Risks: Autonomous agents with tool access can misbehave or be manipulated via prompt injections or unsafe commands. Vulnerabilities in AI agents include unsafe tool access, prompt injections, and adversarial manipulation.
-
Evaluation & Debugging: It’s challenging to trace agent decisions or test performance due to non-deterministic behaviour and limited transparency.
-
Tooling Maturity & Developer Experience: Current frameworks often lack robust support for debugging, monitoring, and scaling agent-based architectures.
Despite these challenges, progress is being made rapidly, and emerging standards are making the space more reliable. As the ecosystem matures, the agentic AI stack has the potential to become a foundational layer in next-gen AI systems.
In Summary: Dissecting the Agentic AI Tech Stack
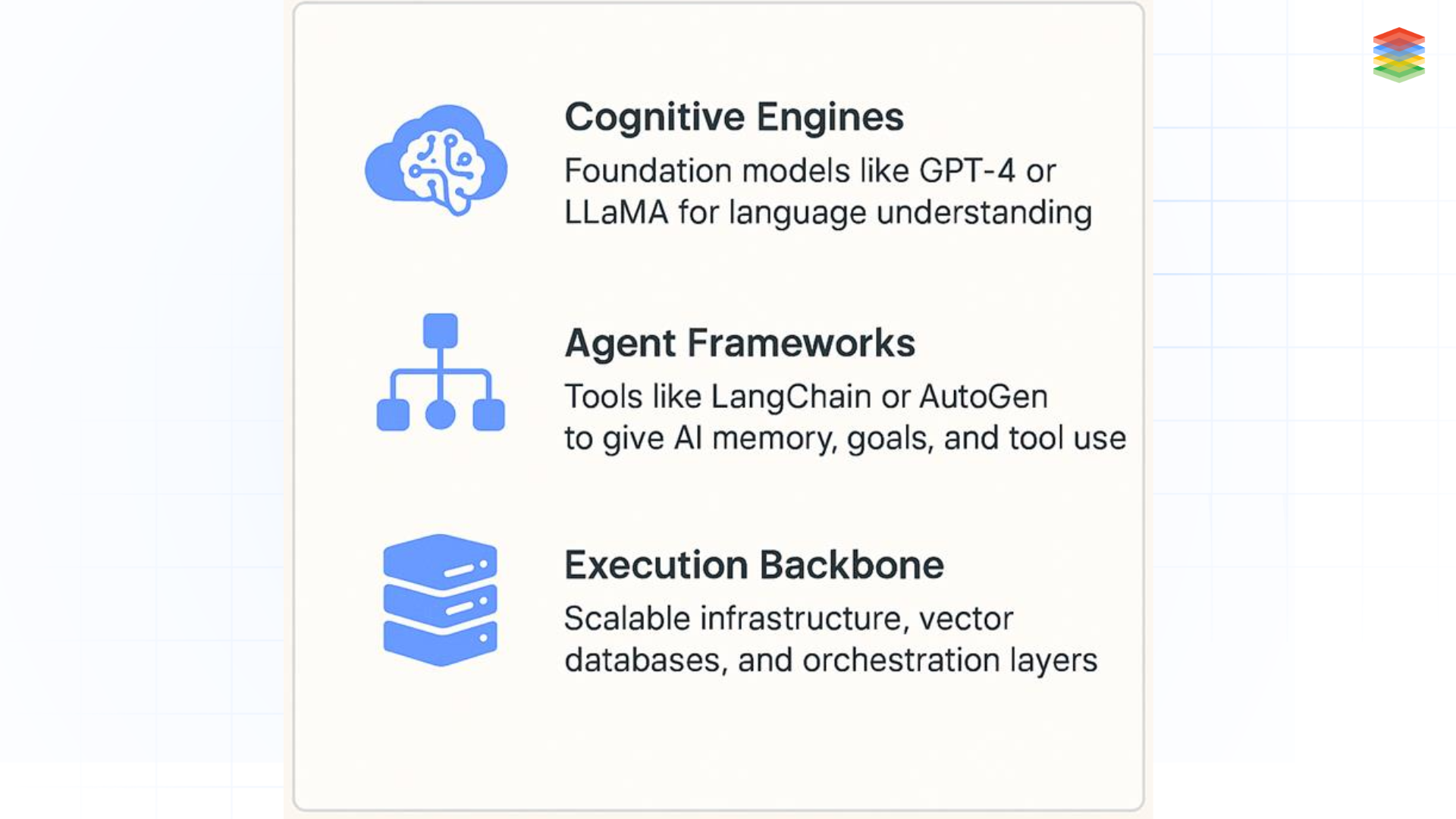
The agentic AI tech stack represents the architecture enabling autonomous AI systems to accomplish complex goals through planning, reasoning, and action. Built upon foundation models (LLMs) that provide core intelligence, this stack incorporates specialised layers for agent frameworks (handling planning, memory, and self-reflection), tool integration (connecting to external services and data sources), execution environments (providing sandboxed runtime and permissions), and orchestration (coordinating multiple agents).
As the technology matures into 2025, we're seeing the emergence of agent-optimized foundation models with built-in tool understanding, standardized integration protocols, enterprise-grade frameworks with compliance features, specialized cloud infrastructure, and sophisticated multi-agent orchestration systems—together forming a comprehensive ecosystem that transforms AI from passive responders to proactive problem-solvers capable of breaking down tasks, using appropriate tools, and achieving objectives with minimal human guidance.
The future lies in Agentic AI for Adaptive Enterprise, where agents not only automate workflows but also guide decision-making with context awareness, trust, and compliance. By building on a robust agentic infrastructure stack, enterprises can unlock the full power of Agentic AI.
What are the primary risks of Agentic AI systems?
Coordination complexity, unsafe tool access, and evaluation difficulty.
.webp?width=1921&height=622&name=usecase-banner%20(1).webp)