Test Driven Development (TDD) is a great approach to software development. TDD is the development of tests before adding a feature in code. This approach is based on the principle that we should write small rather than long codes. In TDD, whenever we want to add more functionality in our codes, we first have to write a test for that. After that, we add new functionality with small code lines combined and then test it with our test. This approach helps us to reduce the risk of encountering significant problems at the production level.
A key practice for extreme programming; it suggests that the code is developed or changed exclusively by the unit testing. Click to explore about, Test Driven Development (TDD) Tools
What is Test Driven Development (TDD)?
Test-driven development is an approach in which we build a test first, then fail the test, and finally refactor our code to pass the test.
Test Driven Development (TDD) Approach
As the name suggests, we should first add the test before adding the functionality in our code. Now, our target is to make the test pass by adding new code to our program. So, we refactor our code to pass the written test. This uses the following process -
- Write a failing unit test
- Make the unit test pass
- Repeat
What is the Test Driven Development Process Cycle?
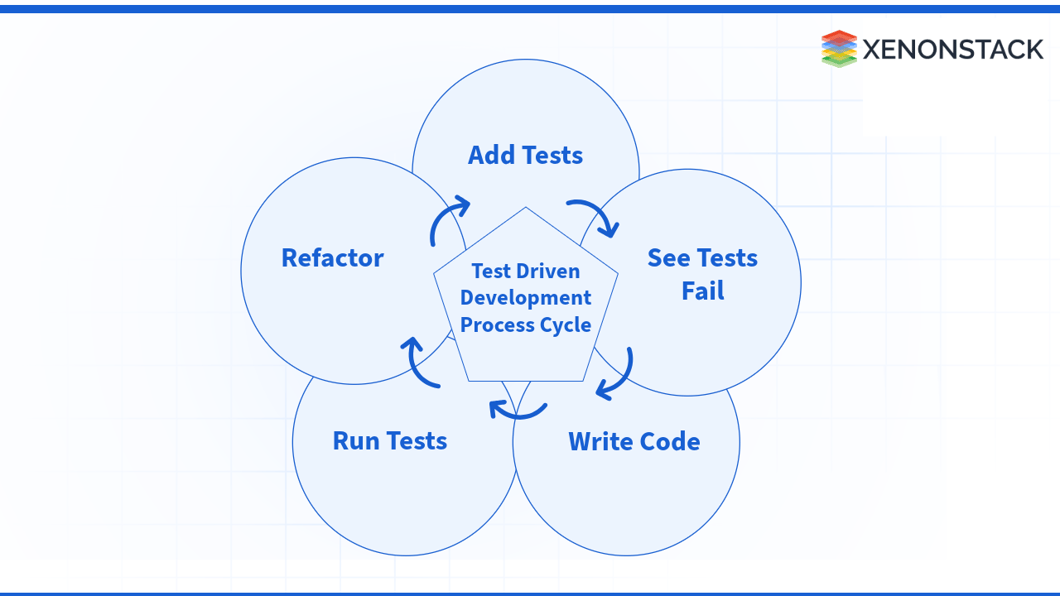 As shown in the flow
As shown in the flow
- First, add tests for the functionality.
- Next, we run our test to fail.
- Next, we write code according to the error we received.
- Then, we run the tests again to see if the test fails or passes.
- Then, refactor the code and follow the process again.
What are the benefits of Test Driven Development (TDD)?
Now, the question arises: why should one opt for the TDD approach? Practicing TDD brings lots of benefits. Some of the benefits are listed below -
-
In TDD, we build tests before adding any new features. That means, in the TDD approach, our entire code is covered under the test. That’s a great benefit of TDD compared to code with no test coverage.
-
In TDD, one should have a specific target before adding new functionality. This means one should be clear about its outcome before adding new functionality.
-
In an application, one method depends on the other. When we write tests before the method, we should have clear thoughts about the interfaces between the methods. This allows us to integrate our method with the entire application efficiently and helps make our application modular, too.
-
The test covers the entire code, so our final application will be less buggy. This is a big advantage of the TDD approach.
What is Acceptance Test Driven Development (ATDD)?
ATDD is short for Acceptance Test Driven Development. In this process, a user, business manager and developer are all involved. First, they discuss what the user wants in his product; then, the business manager creates sprint stories for the developer. After that, the developer writes tests before starting the projects and then starts coding for their product.
Every product/software is divided into small modules, so the developer codes for the very first module then tests it and sees it fails. If the test passes and the code works per user requirements, it is moved to the next user story; otherwise, some changes are made in the coding or program to make the test pass. This process is called Acceptance Test Driven Development.
What is Behavior Driven Development (BDD)?
Behavior-driven testing is similar to test-driven development in that in BDD, tests are written first and tested, and then more code is added to make the test pass. The major area where these two differ is that tests in BDD are written using plain descriptive English grammar.
Tests in BDD aim to explain the application's behaviour and are also more user-focused. These tests use examples to clarify the user requirements better.
Features of Behavior Driven Development (BDD)
- The major change is in the thought process, shifting from analyzing in tests to analyzing in behaviour.
- Ubiquitous language is used; hence, it is easy to explain.
- BDD's approach is driven by business value.
-
It can be seen as an extension of TDD; it uses natural language, which is also easy for non-technical stakeholders to understand.
Database testing can be performed in a web application or desktop because the database can be used in the application. Click to explore about, Database Unit Testing
What are the approaches for Behavior Driven Development (BDD)?
We believe that the role of testing and test automation TDD(Test Driven Development) is essential to the success of any BDD initiative. Testers have to write tests that validate the behaviour of the product or system being generated. The test results formed are more readable by the non-technical user as well. For behaviour-driven development to be successful, it becomes crucial to classify and verify only those behaviours that directly affect business outcomes. Developers in the BDD environment must identify what program to test and what not to test and understand why the test failed. Much like Test Driven Development, BDD also recommends that tests be written first and that the product's functionalities be described in a way that is suited to the requirements.
Behavior-driven Development helps greatly when building detailed automated unit tests because it focuses on testing behaviour instead of implementation. The developer thus has to focus on writing test cases, keeping the synopsis rather than code implementation in mind. By doing this, even when the requirements change, the developer does not have to change the test, input, and output to support them. That makes unit testing automation much faster and more reliable. Though BDD has its own advantages, it can sometimes fall prey to reductions.
Development teams and testers, therefore, need to accept that while failing a test guarantees that the product is not ready to be delivered to the client, passing a test also does not mean that the product is ready for launch. It will be closed when development, testing, and business teams will give updates and progress reports on time. Since the testing efforts are moved more towards automation and cover all business features and use cases, this framework ensures a high defect detection rate due to higher test coverage, faster changes, and timely releases.
What are the benefits of Behavior Driven Development (BDD)?
It is highly suggested that teams and developers adopt BDD for several reasons, some of which are listed below -
- BDD provides very accurate guidance on organizing communication between all the stakeholders of a project, whether technical or non-technical.
- BDD enables early testing in the development process, which means fewer bugs later.
- Using a language understood by all rather than a programming language improves the project's visibility.
- The developers feel more confident about their code and that it won’t break, which ensures better predictability.
A process that enables the developers to write code and estimate the intended behavior of the application. Click to explore about, Unit Testing of ML with Test Driven
Test Driven Development (TDD) with Python
Here, we explore the Test-driven development approach with Python. Python official interpreter comes with the unit test modulePython Unit Testing
These are the main methods that we use with Python unit testing|
Method |
Checks That |
|
a == b |
|
|
assertNotEqual(a, b) |
a != b |
|
assertTrue(x) |
bool(x) is True |
|
assertFalse(x) |
bool(x) is False |
|
a is b |
|
|
a is not b |
|
|
x is None |
|
|
assertIsNotNone(x) |
x is not None |
|
a in b |
|
|
assertNotIn(a, b) |
a not in b |
|
isinstance(a, b) |
|
|
not isinstance(a, b) |
Test-Driven Development (TDD) in Python with Examples
We are going to work on an example problem of banking. Let's say that our banking system introduced a new credit money facility. So we have to add this to our program. Following the TDD approach, before adding this credit feature, we first write our test for this functionality.
Setting Up Environment For Test Driven Development (TDD)
This is our directory structure
Writing Test For Test Driven Development (TDD)
So we write the following code for the unit test in the test/tdd_example.pyimport unittest
class Tdd_Python(unittest.TestCase):
def test_banking_credit_method_returns_correct_result(self):
bank = Banking()
final_bal = bank.credit(1000)
self.assertEqual(1000, final_bal)
Here first, we import the unit test module and then write our test method. We should notice that every test method should start with the test word. Now we run this program
File "/PycharmProjects/TDD_Python/test/tdd_example.py", line 6, in test_banking_credit_method_returns_correct_result
bank = Banking()
NameError: name 'Banking'
is not defined
How do you implement Test Driven Development (TDD) in Python?
So first, we have to create our Banking class in the app/banking_app.py fileclass Banking():
def __init__(self):
self.balance = 0
def credit(self, amount):
pass
import unittest
from app.banking_app
import Banking
class Tdd_Python(unittest.TestCase):
def test_banking_credit_method_returns_correct_result(self):
bank = Banking()
final_bal = bank.credit(1000)
self.assertEqual(1000, final_bal)
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
AssertionError: 1000 != None
Ran 1 test in 0.002 s
FAILED(failures = 1)
class Banking():
def __init__(self):
self.balance = 0
def credit(self, amount):
self.balance += amount
return self.balance
Testing started at 5: 10 PM...
Ran 1 test in 0.001 s
OK
That is the success. So we add credit functionality in our banking and it works as expected But our program is not able to handle some situations, like when a user entered a string instead of the number then our program might crash. So we have to deal with this situation. First, we have to write our test for this
import unittest
from app.banking_app
import Banking
class Tdd_Python(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
self.bank = Banking()
def test_banking_credit_method_returns_correct_result(self):
final_bal = self.bank.credit(1000)
self.assertEqual(1000, final_bal)
def test_banking_credit_method_returns_error_if_args_not_numbers(self):
self.assertRaises(ValueError, self.bank.credit, 'two')
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()Ran 2 tests in 0.002 s
FAILED(errors = 1)
class Banking():
def __init__(self):
self.balance = 0
def credit(self, amount):
amount_type = (int, float, complex)
if isinstance(amount, amount_type):
self.balance += amount
return self.balance
else :
raise ValueError
Testing started at 5: 33 PM...
Launching unittests with arguments python - m unittesttdd_example.py in /PycharmProjects/TDD_Python / test
Ran 2 tests in 0.002 s
OK
Similarly, we can add more functionality to our app by following this approach. By following the same process In the bank, there is more operation like debit money. That means we have to add another functionality of debit also. So we start with the same approach first building test for the debit operation
import unittest
from app.banking_app
import Banking
class Tdd_Python(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
self.bank = Banking()
def test_banking_credit_method_returns_correct_result(self):
final_bal = self.bank.credit(1000)
self.assertEqual(1000, final_bal)
def test_banking_credit_method_returns_error_if_args_not_numbers(self):
self.assertRaises(ValueError, self.bank.credit, 'two')
def test_banking_debit_method_returns_correct_result(self):
final_bal = self.bank.debit(700)
self.assertEqual(1000, final_bal)
def test_banking_debit_method_returns_error_if_args_not_numbers(self):
self.assertRaises(ValueError, self.bank.debit, 'two')
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
AttributeError: 'Banking'
object has no attribute 'debit'
Ran 4 tests in 0.003 s
FAILED(errors = 2)
class Banking():
def __init__(self):
self.balance = 1000
def credit(self, amount):
amount_type = (int, float, complex)
if isinstance(amount, amount_type):
self.balance += amount
return self.balance
else :
raise ValueError
def debit(self, amount):
amount_type = (int, float, complex)
if isinstance(amount, amount_type):
self.balance -= amount
return self.balance
else :
raise ValueErrorTesting started at 5: 44 PM...
Launching unittests with arguments python - m unittest / PycharmProjects / TDD_Python / test / tdd_example.py / PycharmProjects / TDD_Python / test
Ran 4 tests in 0.002 s
OK
Test-Driven Development (TDD) Tools For Python
The best Test best-driven development for Python tools are listed below:
-
nosetest
nosetest is a test runner package. We can easily install this by just pip command $ pip install nose Once it is installed successfully we can run test file simply by just $ nosetests example_unit_test.py the result is as follows
(venv) xenon@dm08:~/PycharmProjects/TDD_Python$ nosetests test/tdd_example.py
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ran 4 tests in 0.001s
OK
-
py.test
py.test is also similar to the nosetest, one thing that makes it good is that it show the output of each test in separate bottom area We can install this by the following command $ pip install pytest Once it is installed successfully we can run test file simply
$ py.test test/example_unit_test.py (venv) xenon @dm08: ~/PycharmProjects/TDD_Python$ py.test test / tdd_example.py === === === === === === === === == test session starts === === === === === === === === === == platform linux--Python 3.4 .3, pytest - 3.2 .5, py - 1.5 .2, pluggy - 0.4 .0 rootdir: /home/xenon / PycharmProjects / TDD_Python, inifile: collected 4 items test / tdd_example.py.... === === === === === === === === 4 passed in 0.09 seconds === === === === === === === === ===
-
unittest
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
-
unittest.mock
In Python, there is a library unitest.mock for testing. This is useful when we try to test a function that requires time to complete. So we use unittest.mock library to mock that function. This library mocks objects and makes assertions about their uses. unitest.mock provides a Mock class, MagicMock and patch(). Here is a quick example of using them: Suppose our credit function takes too much time to complete. So instead of calling the function credit in the test we should mock it to speed up the testing
import unittest
from unittest.mock
import patch
from app.banking_app
import Banking
class TestBanking(unittest.TestCase):
@patch('app.banking_app.Banking.credit', return_value = 1700)
def test_credit(self, credit):
self.assertEqual(credit(700), 1700)
(venv) xenon @dm08: ~/PycharmProjects/TDD_Python$
py.test test / mock.py === === === === === === === === = test session starts === === === === === === === === === === =
platform linux--Python 3.4 .3, pytest - 3.2 .5, py - 1.5 .2, pluggy - 0.4 .0
rootdir: /home/xenon / PycharmProjects / TDD_Python, inifile:
collected 1 item
test / mock.py.
=== === === === === === === === == 1 passed in 0.14 seconds === === === === === === === === ===Next Steps towards Test-driven Development
Connect with our experts to learn how Test Driven Development (TDD) boosts code quality and efficiency. By adopting a test-first approach, teams can build stronger systems, reduce bugs, and automate testing for smoother development. TDD fosters faster feedback, continuous integration, and optimized workflows, ensuring better software and faster delivery
.webp?width=1921&height=622&name=usecase-banner%20(1).webp)


