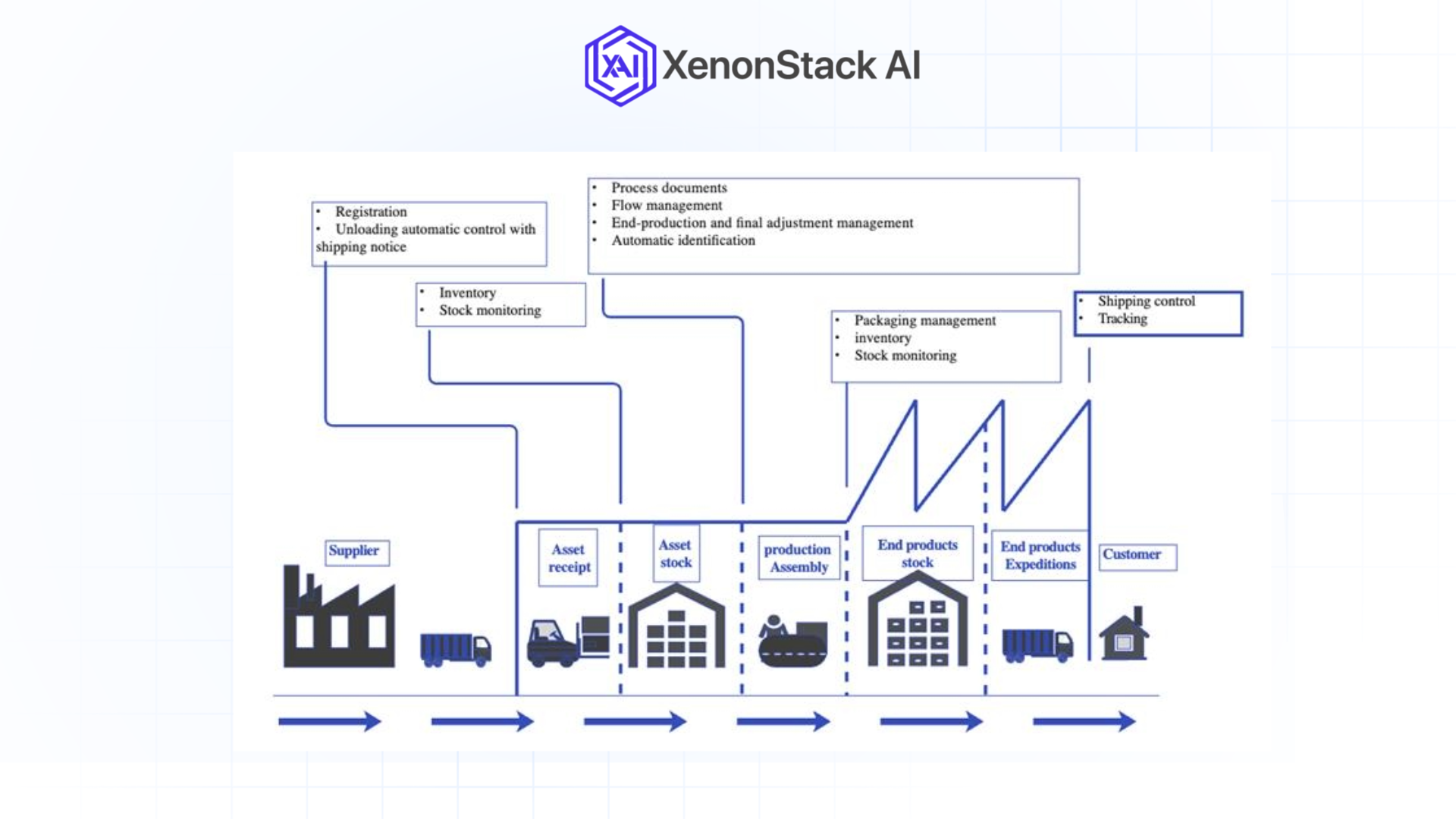
Real-Life Examples of AI in Automotive Supply Chains
Tesla’s AI-Driven Supply Chain
This automaker that prides itself on innovation applies AI in its supply chain process. These speak to the place that the company has built to harness AI solutions for demand forecasting, inventory and order management, and logistics. Tesla also closely checks raw materials, including lithium, which is critical for powering electric vehicles through artificial intelligence. AI is Personalizing Learning Paths for Students.
BMW’s Supply Chain Digitalization
Lastly, BMW uses artificial intelligence throughout its supply chain through the supply chain control tower. In this system, AI constantly observes supply chain events and enhances the chain’s efficiency through real-time controls, enhancing the activity process's credibility. Another aspect of BMW's AI tools is that it uses data from suppliers to help anticipate disruption and find ways to avoid it.
Toyota’s Smart Factory Initiatives
AI is used in Toyota manufacturing plants to improve scheduling, inventory, and production control. AR systems include AI that can take data from sensors and IoT devices on the shop floor to support predictive maintenance decisions. It also ensures suppliers directly interface with production lines, thus enabling an efficient production process.
Advancements in AI Technologies for Supply Chains
-
Predictive Analytics
AI models use historical and real-time data to predict demand, generate a risk profile, and suggest preventive measures. Risk management allows for anticipating and responding to disturbances in the manufacturing process in advance. -
Natural Language Processing or NLP
Conversational interfaces also enable communication between a few manufacturers and suppliers through the analysis of Contracts, emails, and more. This makes communication proper and eliminates rumours that hamper progress.
-
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA automates repetitive tasks, such as order processing and invoice reconciliation, freeing up human resources for strategic activities. Figure 4: Architecture of RPA
Figure 4: Architecture of RPA -
Digital Twins
Digital twins directly mirror the physical supply chain topology created in digital platforms. AI studies these simulations to understand potential problems, improve an organization’s efficiency and model the crisis scenarios. Figure 5: Illustration of digital twin
Figure 5: Illustration of digital twin -
Blockchain Integration
Blockchain, provided by artificial intelligence, facilitates the supply chain by delivering transparency by recording a transaction and helping manage the trace of components. This is especially so when guaranteeing adherence to environments and ethical requirements.
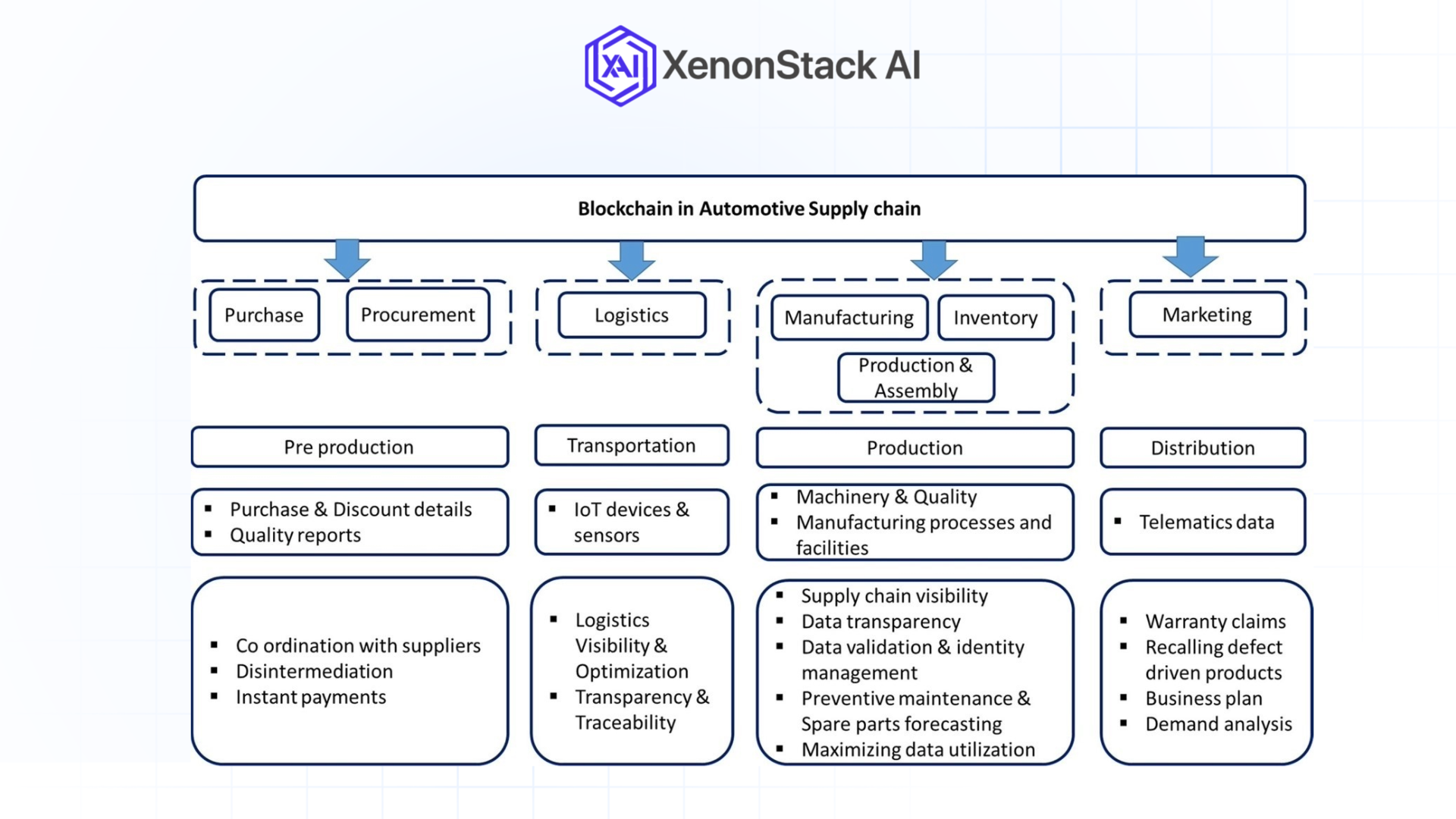
Challenges of AI Implementation in Automotive Supply Chains
-
Data Integration
Coordinating various data sets from suppliers, logistics-providing, and production systems can be problematic.
-
High Initial Costs
AI requires a significant capital investment, including infrastructure, software, and highly trained practitioners.
-
Resistance to Change
Stakeholders may view Such adoption with scepticism either because the tools applied are still new to the organization or because they fear becoming dispensable.
-
Ethical Concerns
AI systems should also prevent prejudice and be designed to offer justice.
Future Trends in AI for Automotive Supply Chains
-
Autonomous Supply Chains
AI will enhance end-to-end supply chain automation, where choices will frequently be made without human interaction.
-
Sustainability Optimization
AI capabilities will create a sustainable supply chain by efficiently reducing wastage and greenhouse gases and encouraging a circular economy.
-
Advanced Collaboration Tools
Manufacturers, suppliers and logistics providers will engage in a smooth business flow through artificially intelligent business platforms.
-
Quantum Computing
AI is the wake of quantum computing that will extend and improve supply chain planning and optimization facilities.
Conclusion for AI-Driven Supply Chain
Implementing AI-driven optimization means that automotive supply chains are transitioning to new high levels of efficacy, robustness, and flexibility compared to a traditional supply chain environment. AI allows manufacturers to improve demand forecasting, logistics, quality control, and risk management. AI innovations are set to transform the automotive supply chain to be more intelligent, greener, and customer-friendly. It is now clear that AI adoption is not only possible but essential to maintaining competitiveness in this electricity sector.
.webp?width=1921&height=622&name=usecase-banner%20(1).webp)