Why Must AI Agent Observability and Evaluation Work Together?
The Lab-to-Production Gap:
Problem: Static evaluation in controlled environments validates functionality but fails to predict production failures caused by:
- Variable load: Performance degrades under concurrent requests or traffic spikes
- Integration complexity: Agents interact with external services (databases, APIs) introducing latency and failure modes
- Multi-agent coordination: Handoffs between agents create communication overhead and potential deadlocks
- Resource constraints: Token limits, API rate limits, memory constraints absent in testing
Traditional Approach Failure:
Evaluation-only strategies produce agents that pass benchmarks but fail in production due to environmental factors. Monitoring-only strategies detect failures reactively but cannot attribute root causes to decision logic vs infrastructure.
Integrated Solution:
- Evaluation establishes baseline capabilities through benchmarks (AgentBench, custom datasets)
- Observability measures production behavior against baseline expectations
- Correlation links evaluation metrics (accuracy, hallucination rate) to observability data (token consumption, latency, error rates)
Business Outcome:
Early detection of performance drift—agents maintaining 95% accuracy in testing but degrading to 80% in production triggers investigation before user impact. Example: E-commerce chatbot latency spike reveals inefficient multi-agent coordination, fixed through prompt optimization identified via trace analysis.
What Are the Core Evaluation Dimensions in AI Agent Observability and Evaluation?
1. Functionality Assessment
Definition: Task completion accuracy across diverse conditions without shortcuts or hallucinations.
Evaluation Methods:
- Benchmark datasets: AgentBench (web navigation, coding, data retrieval tasks)
- Custom test suites: Domain-specific scenarios (payment routing, incident categorization)
- Stress testing: Performance under simulated load (concurrent users, high query volume)
Key Metrics:
- Task success rate (% of goals achieved correctly)
- Hallucination frequency (factually incorrect outputs)
- Response variance (consistency across identical inputs)
Tools: Galileo provides functionality metrics beyond basic accuracy, detecting response drift during long-running sessions.
Production Application: Backend engineers stress-test agents under simulated production load to ensure uptime in systems handling real-time transactions—validating performance before deployment.
2. Reliability Under Production Conditions
Challenge: Agents must maintain performance despite:
- Noisy or incomplete input data
- API failures or timeouts from external services
- Concurrent requests creating resource contention
Evaluation Approach:
- Fault injection: Simulate API timeouts, missing data, malformed inputs
- Load testing: Measure throughput degradation at 2x, 5x, 10x baseline traffic
- Recovery testing: Validate graceful degradation and error handling
Observability Correlation: Reliability scores from evaluation (95% uptime in testing) validated against production metrics (actual 92% uptime reveals integration bottlenecks).
3. Explainability and Decision Transparency
Why It Matters: Production failures require root-cause analysis—unexplained agent decisions block debugging and erode user trust.
Evaluation Methods:
- Decision tree visualization: Inspect reasoning paths in multi-turn interactions
- LLM-as-a-Judge (LaaJ): Semantic evaluation of output quality and reasoning coherence
- Chain-of-thought logging: Capture intermediate reasoning steps for audit
Production Value: Multi-agent systems require explainability to diagnose coordination failures—trace analysis reveals which agent misunderstood context, enabling targeted optimization.
What Metrics Define AI Agent Observability in Production?
1. Latency (Response Time)
Measurement: Time from user input to agent response completion.
Production Targets:
- Interactive applications: <500ms P95 latency
- Background tasks: <2s P99 latency
- Batch processing: throughput-optimized (latency less critical)
Optimization Triggers: Latency spikes indicate:
- Inefficient tool usage (unnecessary API calls)
- Model selection issues (using GPT-4 when GPT-3.5 sufficient)
- Context window overflow (excessive prompt length)
Observability Implementation: OpenTelemetry traces measure end-to-end latency and attribute time to specific operations (model inference, tool execution, data retrieval).
2. Responsiveness (Throughput Under Load)
Measurement: Requests handled per second without quality degradation.
Load Testing Scenarios:
- Normal load: Baseline throughput at typical traffic
- Peak load: Performance during 5x traffic spikes
- Sustained load: Stability over 24-hour high-traffic periods
Auto-scaling Integration: Responsiveness metrics trigger infrastructure scaling—declining throughput at 80% capacity triggers additional agent instances.
3. Context Retention (Multi-Turn Coherence)
Challenge: Agents must maintain conversation history and user preferences across multi-turn interactions—context loss creates disjointed user experiences.
Measurement:
- Coreference accuracy: Correctly resolving pronouns and references to prior turns
- State consistency: Maintaining user preferences and conversation context
- Memory retrieval: Accurately recalling relevant prior interactions
Failure Mode: Agent forgets user's stated budget constraint three turns into conversation, recommending products outside price range—trace analysis reveals context window management issue.

Which Tools Support AI Agent Observability and Evaluation?
Tool Comparison Matrix
| Tool | Primary Focus | Key Capability | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| OpenDeepeval | Modular evaluation | Semantic correctness, hallucination detection, custom metrics | Multi-agent backend testing without heavy infrastructure |
| Confident AI | Scalable benchmarking | Cloud-based eval, red-teaming, A/B testing, multi-modal support | Enterprise-scale evaluation across teams |
| Langfuse | Trace analysis | LangGraph/LangChain tracing, span tracking, feedback loops | Debugging production agent workflows |
OpenDeepeval
-
OpenDeepeval is an open-source framework providing modular semantic correctness, hallucination, and agent-specific evaluation metrics.
-
It supports custom datasets and LaaJ to automate grading, making it suitable for multi-agent backend testing without heavy infrastructure.
-
Developers can extend it for domain-specific use cases such as fintech payment routing validation.
Confident AI
-
Confident AI builds DeepEval as a cloud service for scalable benchmarking, red-teaming, annotation, and A/B testing.
-
It integrates OpenAI and Gemini models and supports multi-modal evaluations including voice and image inputs.
Langfuse
-
Langfuse focuses on tracing LangGraph and other frameworks, tracking spans across LLM calls, tool execution, and user sessions.
-
It enables exporting trace data to Grafana or PostgreSQL and supports explainability logging and feedback loops.
Which tool is best for AI agent observability?
It depends on the use case—OpenDeepeval for modular testing, Langfuse for tracing, Galileo for reliability scoring, and Confident AI for scalable benchmarking.
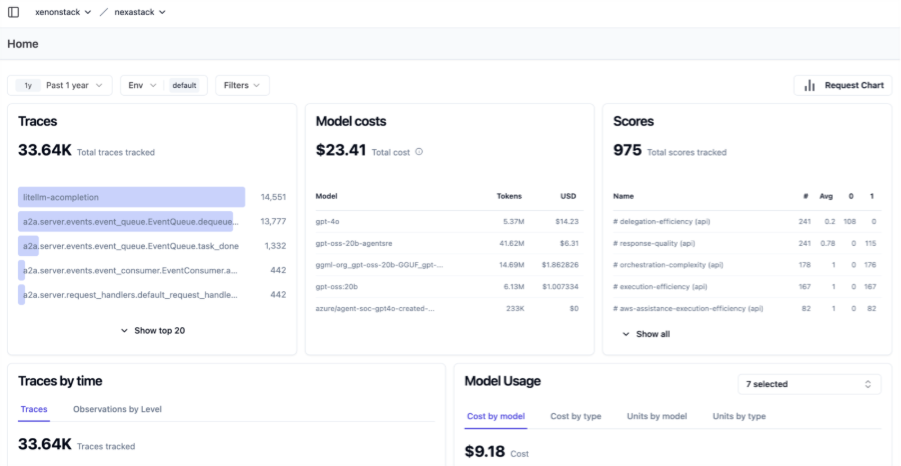
How Are Observability and Evaluation Dashboards Integrated?
The incorporation of dashboards brings together diverse data into integrated perspectives, as seen in the case of Azure AI Foundry, where evaluation scores are superimposed over runtime traces to create holistic agent control, as measured by metrics such as cost and quality. This involves instrumenting code with SDKs from such tools as Langfuse or Galileo, tracing into centralized platforms to query using an SQL-like interface or visual filters.
This configuration in Kubernetes-managed systems aligns the performance of the agents with the infrastructure metrics, enabling the distribution of resources to latency-sensitive tasks.
Unified Dashboard Architecture
Integration Pattern: Combine evaluation scores (from benchmarks) with runtime traces (from production) in centralized dashboards.
Example: Azure AI Foundry Integration:
- Evaluation layer: Benchmark scores (accuracy, latency, cost) from test suites
- Observability layer: Runtime traces showing actual production behavior
- Correlation view: Overlay evaluation expectations with production metrics to identify drift
Implementation Steps:
- Instrumentation: Add SDK calls (Langfuse, Galileo, OpenTelemetry) to agent code
- Data pipeline: Route telemetry to centralized backend (Prometheus, Grafana, custom databases)
- Query interface: SQL-like or visual filters to analyze traces, correlate with evaluation data
- Alerting: Automated alerts when production metrics deviate from evaluation baselines
Kubernetes Integration: In container-orchestrated systems, link agent performance metrics to infrastructure metrics—enables dynamic resource allocation based on agent workload (scale pods when latency-sensitive tasks increase).
How Do Feedback Loops Turn AI Agent Metrics into Meaningful Improvements?
1. Model Routing Optimization
Problem: Using a single model for all tasks wastes resources—simple queries don't require GPT-4 capacity.
Feedback Loop Solution:
- Metric collection: Track model performance (accuracy, latency, cost) per task type
- Routing logic: Dynamically route queries to optimal model based on complexity
- Continuous adjustment: Update routing rules as performance patterns change
Example: LiteLLM Integration: Routes traffic across multiple models (GPT-4, GPT-3.5, Claude) based on responsiveness history—complex queries to GPT-4, simple queries to GPT-3.5, reducing cost while maintaining quality.
2. Self-Improving Agents via Reflection
Mechanism: Agents analyze past sessions using LLM-as-a-Judge, identifying suboptimal decisions and refining behavior.
Implementation in LangGraph:
- Stateful workflows: Maintain session history and decision traces
- Reflection phase: After task completion, agent evaluates own performance
- Behavior modification: Adjust prompts, tool selection, or reasoning strategies based on reflection insights
Production Value: Agents autonomously improve without manual intervention—reducing engineering overhead for performance optimization.
3. DevOps and SRE Integration
SRE Use Case: Incident Management:
- Automated reporting: Metrics from agent-driven incident response generate post-mortem reports
- Pattern detection: Identify common failure modes across incidents, inform process improvements
- Manual effort reduction: Automate log analysis that previously required human review
Continuous Evaluation Cycle (Five-Step Model):
- Define goals: Establish performance targets (SLOs) for agent systems
- Curate data: Collect production metrics and evaluation benchmarks
- Analyze: Correlate evaluation expectations with production reality
- Refine: Adjust prompts, models, or architecture based on insights
- Iterate: Repeat cycle continuously to adapt to changing requirements
Business Outcome: Agents maintain performance alignment with business requirements (SLOs) through continuous feedback, reducing production risks from drift or adversarial inputs.
What metrics matter most for evaluating agent performance?
Task success rate, cost per action, latency, drift signals, and compliance scores.
Conclusion: Building Production-Ready AI Agents Through Integrated Observability and Evaluation
Production AI agents require more than functionality—they must be reliable, explainable, and continuously improving. The integration of evaluation (controlled capability testing) and observability (real-time production monitoring) bridges the lab-to-production gap, enabling:
- Early drift detection: Identify performance degradation before user impact
- Root-cause analysis: Trace failures to specific decisions or integrations via detailed logs
- Resource optimization: Reduce costs through data-driven prompt and model selection
- Continuous improvement: Feedback loops enable agents to self-optimize based on production outcomes
Tools like OpenDeepeval (modular testing), Langfuse (trace analysis) and Confident AI (enterprise evaluation) provide the infrastructure for this integrated approach. Combined with DevOps automation and standardized telemetry (OpenTelemetry), organizations build agent systems that not only function but evolve intelligently based on real-world feedback.
The maturity of observability and evaluation frameworks marks the beginning of autonomous, self-improving AI systems that maintain reliability and efficiency in dynamic production environments.
.webp?width=1921&height=622&name=usecase-banner%20(1).webp)





