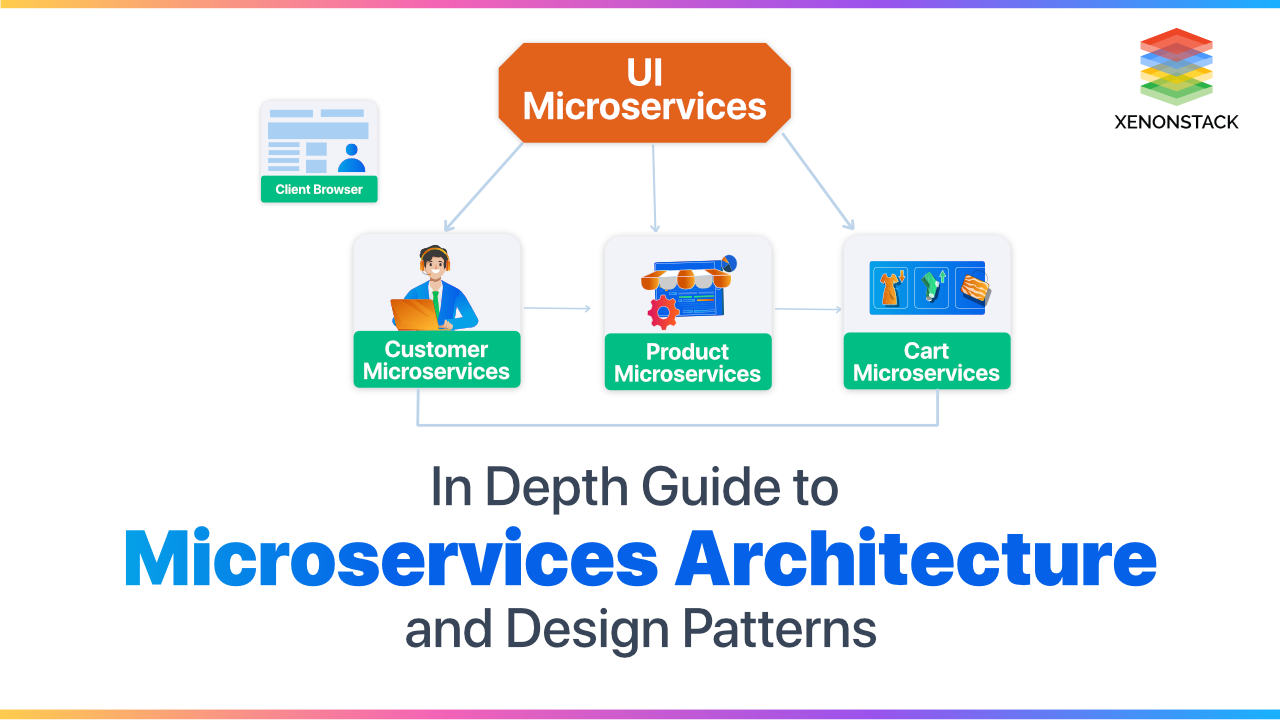
What is Microservices Architecture?
The microservices architecture style is an approach for developing small services, each running in its own process. It enables the continuous delivery/deployment of large, complex applications and allows an organization to evolve its technology stack.
-
Highly Maintainable
-
Loosely Coupled
-
Better Independent Deployability
-
Improved fault isolation
An approach of developing an application by splitting it into smaller services and each module runs in its own process. Click to explore, Microservices Testing Strategies and Processes for Enterprises
Why is Microservices Architecture Important?
Microservices came into the picture for building systems that were too big. The idea behind microservices is that some applications can easily be built and maintained when they are broken down into smaller applications that work together. Each component is continuously developed and separately managed, and the application is then merely the sum of its constituent elements, unlike traditional "monolithic" applications, which are all developed in one piece.
Microservices Architecture Design Patterns
All the services communicate with the API gateway through REST or RPC. These services can be deployed as multiple instances, and the requests can be distributed to these instances. For Separately deployed components, each component is deployed separately. If one component needs changes, others don't have to deploy again. Service componentsServices components communicate with each other via service discovery. Bounded by contexts, it encapsulates the details of a single domain and defines the integration with other domains. It is about implementing a business capability.
What are the benefits of Microservices Architecture Design?
The benefits of Microservices Architecture Design are mentioned below:
-
Asynchronicity.
-
Integration & Disintegration.
-
Completed Deployments.
-
Evolutionary Architecture.
-
Components are deployed.
-
Features are released.
-
Applications consist of routing.
-
It is easier to understand the code—It is easier to distinguish one small service from the flow of the whole service rather than one big code base.
-
Fast Software Delivery - Different developers can develop each service in many languages.
-
Efficient debugging: You don't have to jump through multiple application layers, which is, in essence, better fault isolation.
-
Reusable - Since it is an independent service, it can also be used in other projects.
-
Scalability.
-
Horizontal scaling.
-
Workload partitioning.
-
You don't have to scale the whole project. You only need to scale up that component which needs to scale up.
-
Deployment - We only need to deploy that service that has been changed, not the whole project again.
Cloud-Native Application is an approach for Adopting Cloud Computing features and Capabiblites for building and Deploying the Microservices applications.Source - Why adopt Cloud-Native Strategy?
What are the characteristics of Microservices Architecture Design?
-
Small in size.
-
Messaging enabled.
-
Bounded by contexts.
-
Autonomously developed.
-
Independently deployable.
-
Decentralized.
-
Built and released with automated processes.
What are the types of Microservices Architecture Design Patterns?
There are some main design patterns in which the microservice architecture has been built and designed to work.
-
Strangler Pattern
-
Saga Pattern
-
Aggregator Pattern
-
Event Sourcing
-
Command Query Responsibility Segregation (CQRS)
-
Sidecar Pattern
-
Database per Microservice
Strangler Patterns
Design patterns help decompose applications based on monolithic or microservices approaches. But it will be difficult because breaking them into smaller pieces while alive is a big challenge. So, the Strangler pattern comes into use based on the resemblance that an old system is put behind an intermediary facade. This solution works well with web applications, where requests go back side by side, and for each URI call request, a service can be broken into different domains and hosted as separate services. It can be resolved by creating two separate applications that live parallelly in the same URI space. The newly refactored application strangles(replaces) the original application until shutting off the monolithic application.
Saga Patterns
Ensuring data consistency across services is challenging when each service has its own database and business transactions spanning multiple services. For example, in an e-commerce application where customers have a credit card limit, the application must ensure that a new order will not exceed the customer's card limit. Still, orders and customers are in different databases, so implementing local ACID transactions will take a lot of work. Thus, the saga represents a high-level business process consisting of various sub-requests, updating data within a single service. It can be implemented in two ways:-
-
Choreography is a way to coordinate when there is no centralized way; each service produces and listens to another service's events and decides whether or not to take action.
-
Orchestration (object) tells the participants what transactions to execute and takes responsibility for a saga's decision-making and sequencing business logic.
Aggregator Patterns
In the Microservices framework, the data from each module must be collaborated to produce a combined output. This task cannot be left to the end user because it requires understanding the producer application's internal implementation.
The Aggregator pattern helps to address this challenge. It helps aggregate data from different services and send the final response to the consumer. It can be done in two ways:
-
A composite microservice will call all the required microservices, consolidating and transforming the data before sending it back.
-
An API Gateway acts as an interface that partitions the request to multiple microservices and aggregates the data before sending it to the consumer.
Event Sourcing Patterns
Event sourcing gives a new ordered sequence of events. The application state can be reconstructed by querying the data; to do this, users need to reimage every change to the application's state. Event sourcing is based on the idea that the system should capture any change in an entity's state.
An event store is used to keep track of all of these events. It can serve as a message broker and a database of events, providing services such as the ability to subscribe to events via an API. It can be used in below some conditions.
-
When it is essential to keep the existing data storage.
-
There are no changes in the existing data layer codebase.
-
Transactions are critical to the application's success level.
A model or an architectural paradigm for software that supports the production, detection, consumption of, and reaction to the event or a significant system state change. Taken From Article, Event-Driven Architecture and its Microservices
Command Query Responsibility Segregation (CQRS) Patterns
CQRS suggests splitting the application into two sections: the command side and the query side. The command side handles the Create, Update, and Delete requests. The query side handles the materialized views part ( persists data returned from the view definition query and automatically updates as data changes in the underlying tables). The event sourcing pattern is generally used along with CQRS to create events for any data change that occurs within.
Sidecar Patterns
Every application performs various functions like monitoring, logging, configuration, etc., as individual services. Maintaining these services tightly coupled with the apps can lead to a single point of failure. So, if one component fails, it impacts the entire application. However, every component has dependencies and will need a set of libraries to use the underlying platform. Managing different dependencies and libraries for each element leads to complexity. The solution is the sidecar pattern that allows co-locating additional services within an independent container. The core app and sidecar pattern can perform read and write operations with a shared file system, enabling additional services to be a part of the core app without being tightly coupled.
Database per Microservice
After moving legacy to the microservices, the first thing that comes is the database. Using one extensive database for microservice architecture can act as an anti-pattern due to the tight coupling of services with the database. So, one solution is to provide every microservice with separate or individual databases. Each of the microservices will have a data store restricted for other services.
For example, using a relational database with these three specific options,
-
Tables per service: Each service has an exclusive set of tables inaccessible to other services.
-
Per service schema: Every service has a specific database schema inaccessible to other services.
-
DB server per service: Each service has its database server.
The DevSecOps teams use the microservice architecture while development to ensure Continuous Integration/ Continuous Delivery with increased security measures. Click to explore about, DevSecOps with Microservices Solution
How Microservices Architecture Works?
Microservices are isolated from each other. Each agile team builds individual components. But how do these services work together? To communicate between different microservices, an interprocess communication (IPC) mechanism is needed. Let's understand each component of a microservice architecture.
-
Clients - Different user requests from various devices.
-
Identity Provider- Issues security tokens or authenticates clients and users.
-
API Gateway - Handles requests from various clients.
-
Static Content—A server delivers the same file to each user and houses the system's content.
-
Service Discover - This is used to find the communication route between microservices.
-
Content Delivery Network: This is a geographically distributed group of servers that works together to provide fast delivery of internet content.
-
Remote Service - This is used to enable remote access to information.
How to adopt Microservices Architecture?
So, how do we ensure that the organization adopts the microservices architecture or has already adopted it? If a team implements a service-oriented architecture (SOA), it is already following modularity and message-based communication. On the other hand, if a team follows DevOps practices, automated deployments are already there. Moreover, it builds the culture of microservices architecture within an organization. Implementing the microservice architecture is not always essential when it comes to business goals.
The focus should be on unlocking the business values by improving the architecture more. Most of the time, it means building an application with more resilience and changeability than ever before. The microservices architecture can't be achieved with only a set of patterns, processes, or tools. The team must focus on the goal itself --> A system that can make change easier. The organization needs to focus on speed and safety, and it should find the perfect balance between them at scale.
What are the best practices of Microservices Architecture?
Some essential requirements to do best practices to adopt Microservices --
Independent Teams - Create an environment where teams can get more done without coordinating with other teams.
-
Focus on Automation - Automate everything.
-
Built for Resilience - Ensures failure doesn't impact too much.
-
Simplify the Maintenance - Have proper guidelines and documentation for each service.
-
Provide Flexibility - Give teams the freedom to do what's right for their services.
Tools for Managing Microservices Architecture
-
API Gateway -Centralize API management. Azure API Management and Amazon API Gateway can be used as API gateways.
-
Cloud Infrastructure or Serverless-AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and OpenStack.
-
Containers, Clustering, and Infrastructure as Code -Docker, Kubernetes.
-
Enterprise Service Bus -Red Hat JBoss Fuse, Microsoft BizTalk.
-
Service Discovery -Etcd, Apache Zookeeper, Consul.
Holistic Strategy
-
Explore more about Serverless Microservices
-
Get more information about Serverless and Microservices for Blockchain apps.
Next Steps in Microservices Architecture
Talk to our experts about implementing Microservices Architecture and exploring how industries and departments leverage design patterns to streamline workflows and enhance decision-making. Utilize Microservices to automate and optimize IT support and operations, improving efficiency and responsiveness.
.webp?width=1921&height=622&name=usecase-banner%20(1).webp)


