Manufacturing is undergoing a transformative shift. After decades of automation guided by the principles of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, we are now stepping into Industry 5.0, an era emphasising the synergy between human capabilities and intelligent systems. The central focus is no longer just on automation; it’s about creating adaptive, intelligent, and resilient systems that evolve.
At the forefront of this evolution is Agentic AI—a framework grounded in autonomous, intelligent agents capable of observing their environment, making decisions, learning continuously, and collaborating with both machines and humans. This blog explores how Agentic AI revolutionises manufacturing through detailed architectural insights, use cases, real-world examples, implementation strategies, and a deep dive into the associated benefits and challenges.
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to a system architecture composed of intelligent software agents that can:
-
Perceive real-time data from their environment
-
Analyze and contextualize this data
-
Make informed, autonomous decisions
-
Execute actions aligned with operational or strategic objectives
These agents operate individually or in coordinated clusters to solve complex, interdependent problems typical in dynamic manufacturing environments.
Core Characteristics of Agentic AI:
-
Autonomy: Executes tasks with minimal human intervention
-
Goal-Driven: Prioritizes long-term goals alongside short-term tasks
-
Proactive: Anticipates problems and opportunities, not just reacting to them
-
Collaborative: Seamlessly works with other agents and human users
-
Context-Aware: Adjusts behaviour based on environmental shifts
This represents a departure from traditional AI models that often require human validation to trigger decisions or actions.
Agentic AI vs. Traditional AI in Manufacturing
|
Feature
|
Traditional AI
|
Agentic AI
|
|---|---|---|
|
Behaviour
|
Reactive
|
Proactive and autonomous
|
|
Focus
|
Solves isolated tasks
|
Manages workflows end-to-end
|
|
Decision-Making
|
Uses predefined rules
|
Learns and adapts in real-time
|
|
Collaboration
|
Limited to single systems
|
Coordinates with agents and humans
|
|
Execution
|
Suggests actions for humans
|
Takes independent actions where applicable
|
Agentic AI enables continuous self-improvement through iterative learning and contextual adaptation—turning machines into true collaborators in operations.
Key Use Cases of Manufacturing
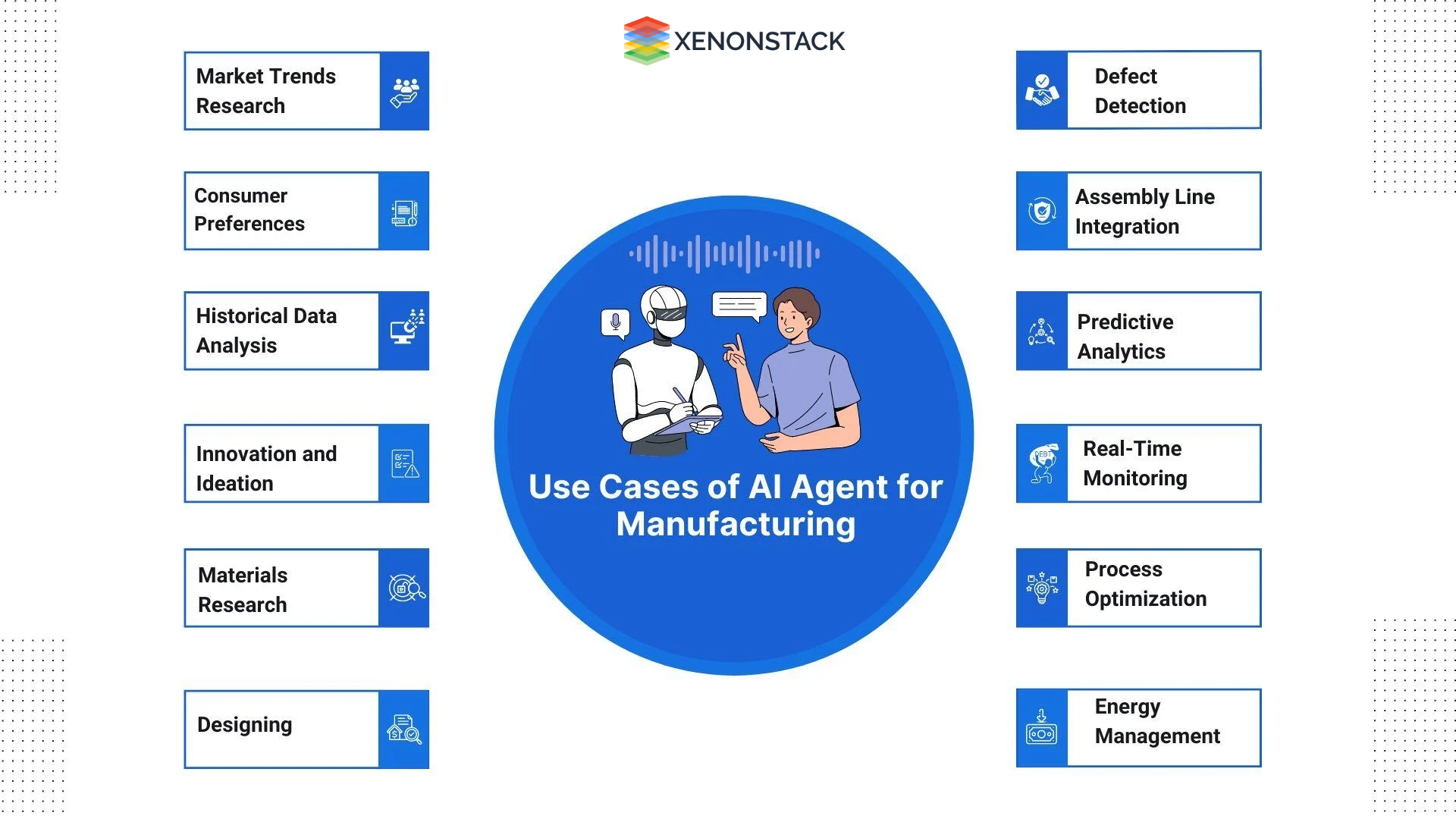 Fig 1: Use Cases of Manufacturing
Fig 1: Use Cases of Manufacturing1. Autonomous Scheduling and Production Orchestration
Challenge: Static production planning leads to inefficiencies during disruptions like equipment failure or supply shortages.
Agentic Solution:
-
Task agents monitor machine status, order flow, and operator availability in real time.
-
Scheduling agents dynamically reallocate tasks based on operational priorities.
-
Interface agents update MES and ERP systems automatically
-
Operators receive alerts through intuitive dashboards
Outcome: A major automotive supplier using agent-based orchestration achieved a 23% reduction in idle time and significantly improved on-time delivery.
2. Predictive Maintenance with Intelligent Agents
Challenge: Scheduled maintenance is not cost-efficient and often fails to prevent unexpected breakdowns.
Agentic Solution:
-
Perception agents gather sensor data from equipment continuously.
-
Diagnostic agents identify early-stage anomalies using ML models.
-
Execution agents trigger service orders, notify technicians, and track part inventory.
Outcome: GE Digital’s Predix APM platform has helped reduce turbine outages by over 30% annually, showcasing the value of intelligent, proactive maintenance.
3. Adaptive Quality Control
Challenge: Defect detection is traditionally reactive, resulting in waste and rework.
Agentic Solution:
-
Vision agents inspect components using advanced imaging and ML classification.
-
Analysis agents detect defect trends and adjust manufacturing parameters in real-time.
-
Human involvement is reserved for exception handling and strategy alignment.
Outcome: Bosch implemented agentic quality control to reduce scrap by 40%, boosting overall throughput and consistency.
4. Real-Time Supply Chain Management
Challenge: Conventional supply chains are too rigid to handle real-time changes in demand or disruptions.
Agentic Solution:
-
Monitoring agents track vendor performance, transportation status, and inventory.
-
Optimization agents reroute orders or select alternative suppliers based on real-time data.
-
Communication agents align internal logistics and procurement workflows.
Outcome: Schneider Electric’s EcoStruxure platform leverages these agents to drive supply chain responsiveness and reliability.
5. Collaborative Robotics and Safety Enhancement
Challenge: Pre-programmed robots lack flexibility and can present safety risks to workers.
Agentic Solution:
-
Safety agents analyze proximity data and adjust cobot behaviour dynamically.
-
Coordination agents plan shared tasks with human collaborators.
-
Compliance is monitored continuously to meet safety standards.
Outcome: using FANUC robots and agentic control systems, BMW improved collaboration on assembly lines while enhancing worker safety.
The Architecture of Agentic AI in Manufacturing
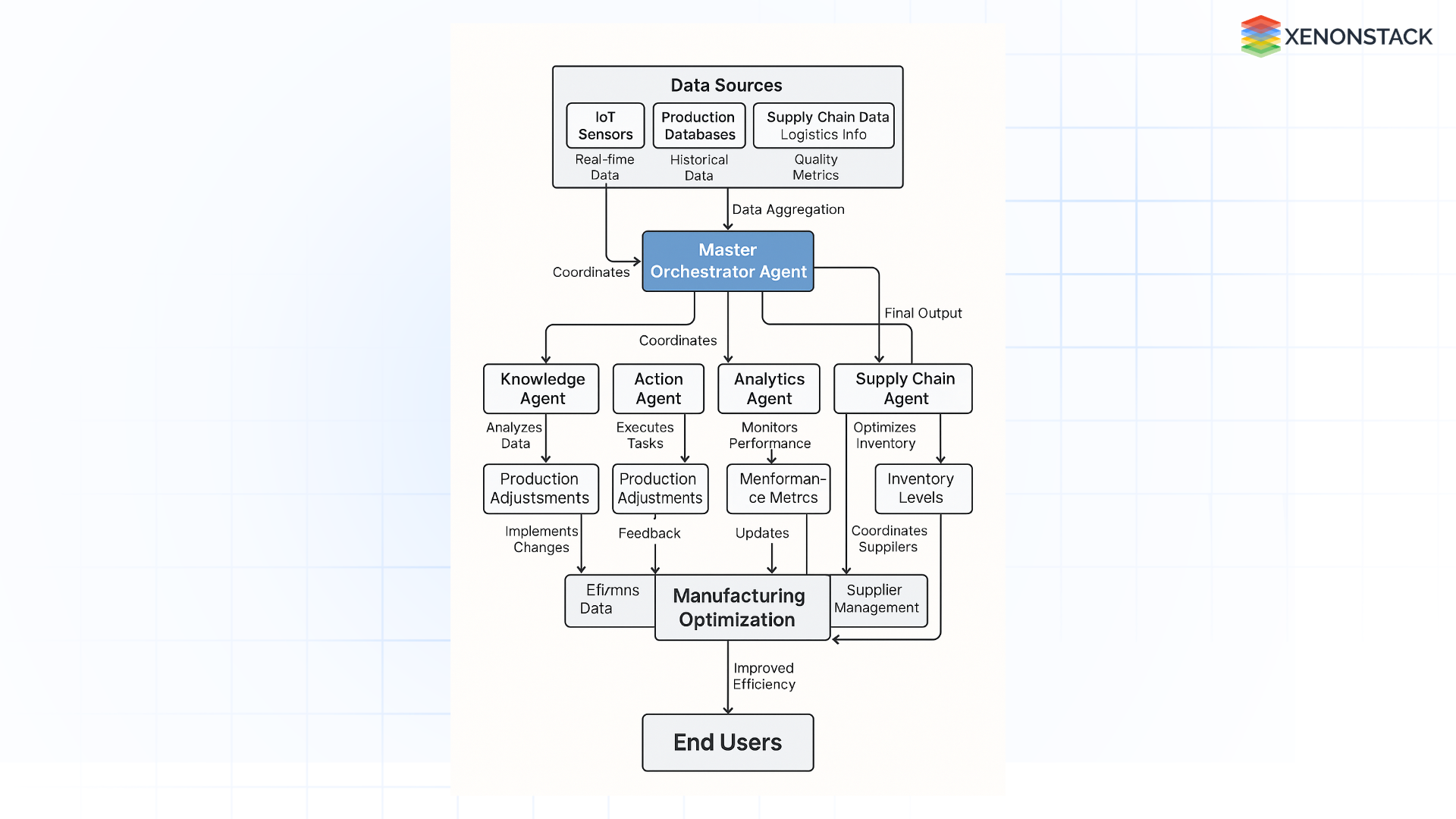 Fig 2: Architecture of Manufacturing
Fig 2: Architecture of ManufacturingImplementing Agentic AI requires a robust, layered system architecture:
Data Collection Layer
Captures data from sensors, controllers, MES, ERP, and external systems
Perception Layer
Applies ML models for event detection, visual inspection, and anomaly recognition
Agent Layer
-
Task Agents: Manage discrete operations like inspections or order sequencing.
-
Cognitive Agents: Refine strategies based on feedback loops.
-
Interface Agents: Facilitate interaction with humans and enterprise software.
Execution Layer
Interfaces with robotics, actuators, and production equipment to implement decisions
Governance and Security Layer
Maintains traceability, compliance, access control, and audit trails
Benefits of Agentic AI in Manufacturing
-
Enhanced Operational AgilityAgents respond instantly to shifts in production demand, inventory levels, and labor availability.
-
Reduction in Operational CostsSavings from predictive maintenance, reduced waste, and optimized energy consumption.
-
Empowered WorkforceSkilled workers can focus on problem-solving and innovation by offloading routine tasks to agents.
-
Resilient and Reliable SystemsAgentic coordination ensures continuity even during unexpected disruptions.
-
Intelligent ScalabilityNew agents can be deployed modularly as operations expand or diversify.
Implementation Challenges and Their Mitigation
|
Area
|
Challenge
|
Solution
|
|
Data Management
|
Fragmented or low-quality data undermines agent accuracy
|
Invest in centralized data platforms and real-time ETL
|
|
Legacy Systems
|
Incompatibility with modern integration protocols
|
Use API wrappers and middleware for interoperability
|
|
Workforce Adaptation
|
Cultural resistance to AI-driven decisions
|
Introduce gradual adoption with training and hybrid pilots
|
|
Transparency
|
Difficulty in understanding agent logic
|
Design for explainability using traceable decision logs
|
|
Security
|
Expanded attack surface with autonomous agents
|
Adopt strict access control and encrypted communications
|
Key Manufacturing Trends with Agentic AI
The global manufacturing ecosystem is rapidly evolving—fueled by unprecedented technological acceleration and demands for resilience, efficiency, and sustainability. In this dynamic environment, Agentic AI and autonomous agents are emerging as the backbone of intelligent operations, moving beyond task automation to decision autonomy. Here's a comprehensive view of how key trends are being redefined through agent-based systems:
1. Hyperautomation and Smart Manufacturing 2.0
Traditional View: Automation has long been about reducing manual labor through robotics and control systems. However, these systems often lack context awareness and adaptability.
Agentic Shift: In Smart Manufacturing 2.0, autonomous AI agents act as cognitive collaborators embedded within production environments.
-
What’s Changing: Agents now orchestrate end-to-end production lines—not just executing pre-set instructions but learning, adapting, and making real-time goal-aligned decisions.
-
Example: A “production optimization agent” continuously learns from machine data, weather conditions, workforce availability, and order urgency to reconfigure workflows autonomously.
-
Why It Matters: This transforms static automation into adaptive autonomy, increasing throughput by 20–30% while reducing downtime.
2. Sustainable and Green Manufacturing
Traditional View: Sustainability was managed through manual reporting, occasional audits, and broad carbon-reduction targets.
Agentic Shift: Carbon intelligence agents are now embedded into every process node—from energy procurement to waste disposal—ensuring proactive, real-time sustainability.
-
What’s Changing: Autonomous agents calculate scope 1, 2, and even scope 3 emissions across supply chains, making eco-optimized decisions without waiting for human analysis.
-
Example: A “green sourcing agent” identifies suppliers with the lowest carbon impact and auto-recommends alternatives during procurement.
-
Why It Matters: Manufacturers can align with ESG mandates in real time, meet net-zero targets faster, and avoid greenwashing risks.
3. Predictive to Prescriptive Maintenance with Autonomous Agents
Traditional View: Predictive maintenance systems detect anomalies and alert engineers.
Agentic Shift: With Agentic AI, maintenance systems don’t just alert—they diagnose, decide, and act.
-
What’s Changing: Agents leverage sensor data, maintenance logs, and failure simulations to prescribe solutions and initiate preventive actions.
-
Example: A “self-healing maintenance agent” shuts down a faulty component, re-routes production, and schedules a drone-assisted repair autonomously.
-
Why It Matters: Reduces downtime by 50%, improves asset life cycles, and eliminates reactive maintenance.
4. Reshoring, Localization, and Resilient Supply Chains
Traditional View: Reshoring was considered a cost trade-off to mitigate geopolitical and shipping risks.
Agentic Shift: Supply chain agents enable intelligent reshoring by dynamically adapting to local constraints and global shocks.
-
What’s Changing: These agents model geopolitical risks, labor availability, and lead times to optimize sourcing and routing constantly.
-
Example: A “logistics coordination agent” reroutes raw material sourcing from Asia to Mexico in real time after sensing port congestion and risk alerts.
-
Why It Matters: Increases resilience, minimizes disruption, and shortens time-to-market even during crises.
5. Autonomous Decision-Making Through Data-Driven Operations
Traditional View: Data analytics was dashboard-driven, where humans interpreted insights to decide.
Agentic Shift: Now, goal-driven agents ingest multimodal data (text, vision, sensor, video) and autonomously act toward organizational KPIs.
-
What’s Changing: Factories rely on autonomous decisions triggered by agentic evaluation instead of insights.
-
Example: A “production intelligence agent” monitors MES, inventory, demand, and HR data daily to rebalance shifts, production rates, and machine usage.
-
Why It Matters: Enhances agility, reduces decision latency, and ensures consistent alignment to OKRs.
6. Cybersecurity as a Core Operational Pillar
Traditional View: Cybersecurity in OT environments was largely reactive—dependent on antivirus tools, firewalls, and annual audits.
Agentic Shift: Security agents operate 24/7, autonomously detecting threats, remediating vulnerabilities, and simulating breach scenarios.
-
What’s Changing: Agents are no longer reactive—they predict and contain attacks proactively across IT and OT networks.
-
Example: A “zero-trust agent” revokes access to a CNC machine after identifying unusual behaviour patterns in machine code injections.
-
Why It Matters: Protects operational continuity and intellectual property in a hyper-connected manufacturing setup.
7. Human-Agent Collaboration and Workforce Augmentation
Traditional View: Workers interacted with machines through HMIs and dashboards. The training was manual and experience-based.
Agentic Shift: Co-pilot agents now assist, coach, and collaborate with human workers using AR/VR, NLP, and vision-based tools.
-
What’s Changing: Agents guide technicians during assembly or maintenance, offering real-time instructions, simulations, and corrections.
-
Example: A “skill enhancement agent” detects operator hesitation, offers video-based guidance, and even switches machine modes for safety.
-
Why It Matters: Reduces onboarding time, minimizes human errors, and ensures the democratization of technical expertise.
8. Digital Twins Reinvented with Interactive Agent Layers
Traditional View: Digital twins were static or reactive models used for planning or monitoring.
Agentic Shift: Now, digital twins are live, adaptive environments powered by multi-agent systems.
-
What’s Changing: Agents simulate alternative production scenarios, experiment with optimization strategies autonomously, and validate before deployment.
-
Example: A “simulation agent” analyzes the impacts of supply chain disruption on a virtual twin and offers reallocation strategies without halting live production.
-
Why It Matters: Enables risk-free testing, strategic forecasting, and agile operations at scale.
The convergence of Agentic AI, autonomous agents, and advanced manufacturing platforms is ushering in the Age of Intelligent Autonomy. Manufacturers who embed these agentic frameworks into their core operations will unlock new speed, safety, adaptability, and innovation thresholds. This isn’t just digital transformation—it’s agentic orchestration of the entire value chain.
How Explainable AI Transforms Manufacturing Operations
 Fig 3: Explainable AI Transform Manufacturing
Fig 3: Explainable AI Transform Manufacturing
Artificial intelligence is central to modern manufacturing decision-making—from predictive maintenance and quality control to supply chain optimization. However, as AI models become more complex, a major concern arises: How do we trust the decisions made by these models? This is where Explainable AI (XAI) steps in, offering transparency, accountability, and actionable insights.
1. Enhancing Trust in AI-Driven Decisions
Traditional AI models often function as "black boxes," delivering outputs without clarity on how decisions are made. In contrast, Explainable AI offers clear reasoning behind predictions, which helps manufacturing leaders, engineers, and floor managers understand:
-
Why a machine was flagged for preventive maintenance
-
Why are certain batches identified as defective
-
What factors are influencing energy inefficiencies
XAI bridges the gap between AI systems and human operators by providing interpretable models.
2. Improving Quality Assurance and Compliance
Traceability and compliance are non-negotiable in highly regulated industries, such as automotive, pharmaceutical, and aerospace manufacturing. Explainable AI makes it easier to:
-
Justify inspection results to auditors and stakeholders
-
Document decisions for ISO or regulatory audits
-
Detect root causes of anomalies with contextual understanding
This reduces compliance risks and improves quality reporting with confidence.
3. Empowering Operators with Real-Time Insights
Explainable AI isn’t just for data scientists. It empowers on-ground personnel by providing real-time visual explanations for:
-
Equipment behaviour anomalies
-
Production slowdowns
-
Yield fluctuations
This democratizes AI insights across the organization and promotes faster decision-making at all levels.
4. Accelerating Root Cause Analysis and Continuous Improvement
By revealing the "why" behind anomalies or downtime events, XAI accelerates:
-
Root cause analysis in quality failure investigations
-
Lean Six Sigma and Kaizen initiatives
-
Predictive and prescriptive maintenance actions
This enables continuous improvement and faster resolution of production issues, ultimately boosting operational efficiency.
5. Supporting Ethical and Responsible AI Use
Explainability fosters responsible AI adoption by identifying biases in data or model decisions. In manufacturing environments where AI may influence hiring, worker safety, or environmental controls, XAI ensures:
-
Ethical decision-making
-
Bias detection and mitigation
-
Transparent stakeholder communication
Why Responsible AI Matters in Manufacturing?
As the manufacturing industry increasingly adopts AI to optimize operations, enhance productivity, and drive innovation, the need for Responsible AI becomes paramount. Responsible AI ensures that manufacturers remain accountable, ethical, and human-centric while embracing automation and intelligence.
A responsible AI framework in manufacturing empowers organizations to:
-
Ensure Predictability, Agility, and Resiliency: AI helps reduce operational complexity, costs, and risks while ensuring the continuity of business processes during unexpected disruptions.
-
Enhance Transparency and Visibility: With complete visibility into systems and workflows, manufacturers can reduce downtime and react swiftly to anomalies.
-
Deliver on Customer Promises: Leveraging Explainable AI enables manufacturers to address customer queries transparently and uphold trust.
-
Boost Manufacturing Efficiency: AI-driven automation accelerates production cycles, reduces errors, and increases overall output—ultimately improving revenue.
-
Drive AI-Driven Insights: AI enables a granular understanding of product performance and customer expectations by analysing behavioural patterns, product demand, and recall data.
-
Keep Systems Human-Centered: Responsible AI ensures human oversight in decision-making, preserving social well-being and preventing the loss of control to autonomous systems.
Agentic AI signals a paradigm shift in manufacturing—from static automation to adaptive autonomy. It enables organizations to embed decision-making capabilities directly into their systems, workflows, and machinery. By doing so, manufacturers improve efficiency and responsiveness and achieve greater alignment with strategic goals like sustainability, agility, and innovation.
This is not theoretical. Global leaders like Bosch, Siemens, GE, and Schneider Electric are already integrating agent-based intelligence into their operations, unlocking measurable improvements across key performance indicators.
Next Steps in Manufacturing Industry
Talk to our experts about implementing a compound AI system. Learn how industries and various departments use Decision Intelligence to become decision-centric. By leveraging Generative AI, businesses in the manufacturing industry can automate and optimize operations, driving efficiency and enhancing responsiveness in IT support and other processes.
.webp?width=1921&height=622&name=usecase-banner%20(1).webp)




