How Snowflake and Iceberg Complement Each Other
Snowflake and Iceberg complement each other by combining Snowflake’s high-performance query capabilities with Iceberg’s robust data management features. While Snowflake is known for its ability to perform fast, scalable analytics, Iceberg handles large datasets' storage, versioning, and metadata management. By integrating these two platforms, organizations can take advantage of both.
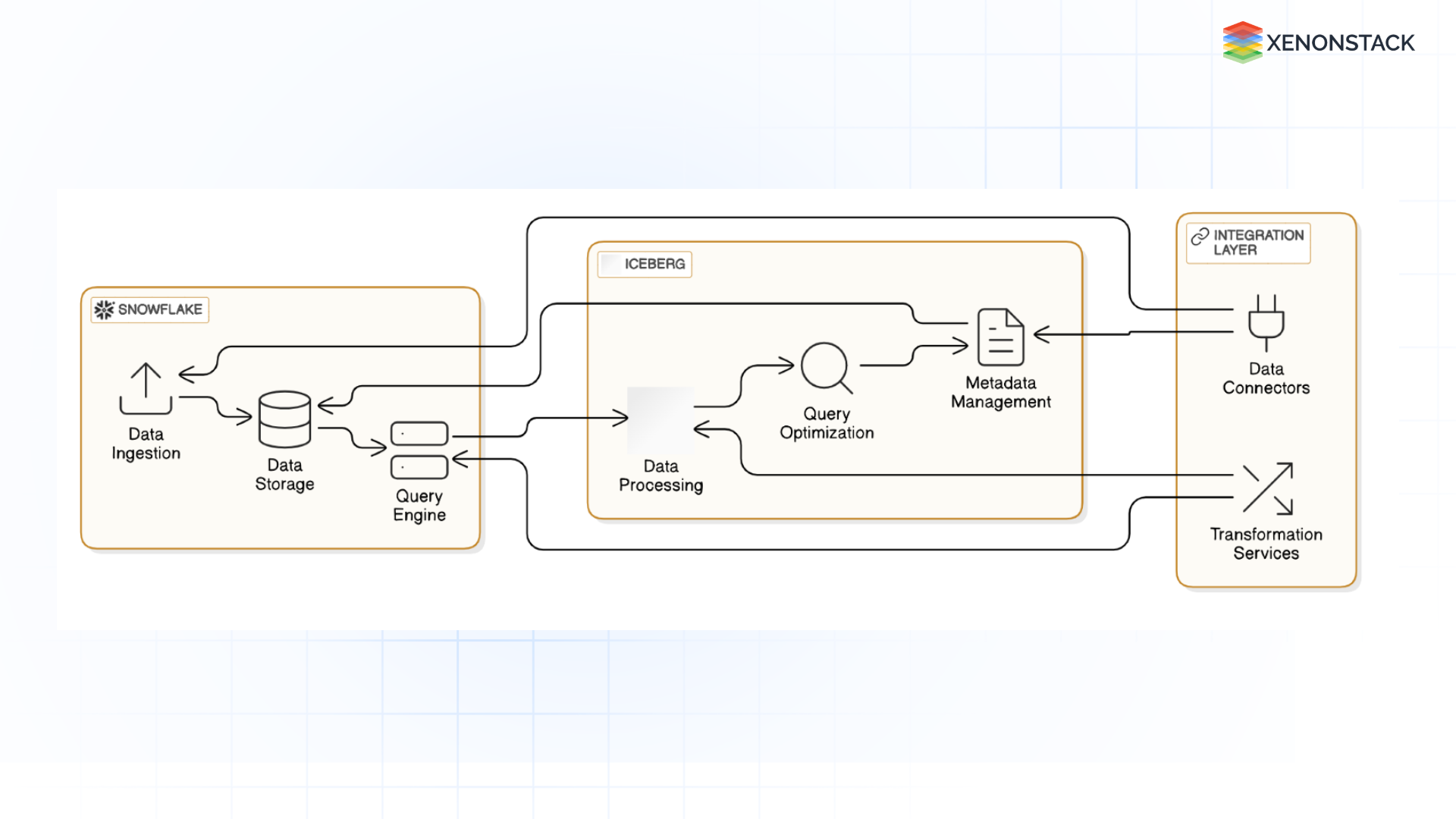 Fig 1: Snowflake and Iceberg Complement Each Other
Fig 1: Snowflake and Iceberg Complement Each Other
For example, Iceberg stores data in a cloud storage system like Amazon S3, and Snowflake’s external tables can query this data without moving or copying it into Snowflake’s native storage. This integration allows businesses to use Snowflake’s advanced querying and analytics while keeping the data in a scalable, cost-effective format like Iceberg.
Use Cases and Benefits of Snowflake and Iceberg Integration
The integration of Snowflake and Iceberg brings numerous benefits to organizations, such as:
-
Efficient Data Management: Iceberg helps organize large datasets, track changes, and evolve schemas without impacting performance. Snowflake’s powerful query engine makes it easy to analyze this data at scale.
-
Faster Data Access: By leveraging Snowflake’s compute capabilities and Iceberg’s efficient data storage, users can query massive datasets with minimal delay.
-
Cost Efficiency: The ability to store data in Iceberg tables on cloud storage platforms like Amazon S3 allows organizations to reduce storage costs while maintaining fast, reliable access to their data.
-
Flexible Analytics: Businesses can perform complex analytics across data stored in Iceberg tables without needing to transform or migrate the data, making gaining insights from various data sources easier.
Interoperability Between Snowflake and Iceberg
Connecting Snowflake Open Catalog with Iceberg Tables
One key benefit of Snowflake and Iceberg interoperability is the ability to use the Snowflake Open Catalog to manage and access Iceberg tables. The catalog provides a centralized repository for Iceberg table metadata, essential for querying and managing large datasets across platforms.
 Fig 2: Connecting Snowflake Open Catalog with Iceberg Tables
Fig 2: Connecting Snowflake Open Catalog with Iceberg Tables
To connect Snowflake Open Catalog with Iceberg tables, you can follow these basic steps:
Setup
Step 1. Create Snowflake Open Catalog Account, Connections, Roles
- Create a Snowflake Open Catalog account
- Create a catalog
From the Connections page:
-
In the Principals tab, create three service connections named spark_analyst, spark_engineer, and snowflake_engineer.
-
In the Roles tab, create three principal roles named spark_analyst_role, spark_engineer_role and snowflake_engineer_role.
From the snowflake_catalog page, in the roles tab
Create three catalog_role named table_all,table_reader_refined, and snowflake_catalog_role with the following privileges
table_all:
-
Catalog:
-
NAMESPACE_LIST
-
TABLE_LIST
-
TABLE_READ_DATA
-
CATALOG_READ_PROPERTIES
table_reader_refined:
-
Catalog:
-
NAMESPACE_LIST
-
Namespace BUILD_DB.REFINED
-
NAMESPACE_LIST
-
TABLE_LIST
-
TABLE_READ_DATA
snowflake_catalog_role:
-
Catalog:
-
CATALOG_MANAGE_CONTENT
Assign catalog roles to principal roles:
-
table_all: spark_engineer_role
-
table_reader_refined: spark_analyst_role
-
snowflake_catalog_role: snowflake_engineer_role
Step 2. Create External Volume
Create and configure an external volume for Snowflake Dynamic Iceberg tables to write data and metadata.
Step 3. Create Tables
Execute the statements in sampledata.sql (if having) to create tables and schemas in a dedicated database. If you choose to use different object names than the provided SQL, you may need to replace the following values with your own:
-
EXTERNAL_VOLUME
-
CATALOG
-
BASE_LOCATION
-
CATALOG_SYNC
Step 4. Load Data
Use the following .csv files and load data into respective tables using Snowsight
Benefits of Data Interoperability
The interoperability between Snowflake and Iceberg provides several benefits:
-
Seamless Data Access: Snowflake users can access data stored in Iceberg tables without needing to move or transform it, improving efficiency and reducing data duplication.
-
Improved Data Governance: By centralizing metadata in the Snowflake Open Catalog, organizations can better manage data access and track data lineage, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
-
Enhanced Collaboration: Snowflake’s data-sharing capabilities, combined with Iceberg’s versioning and metadata tracking, enable teams to collaborate on data analysis while ensuring consistency and accuracy.
Real-Time Data Access and Querying Across Platforms
With Snowflake and Iceberg working together, organizations can query and analyze data in real-time across platforms. Whether the data is stored in Snowflake or Iceberg, Snowflake's powerful query engine ensures fast performance, enabling users to make data-driven decisions quickly.
Use Cases of Interoperability
-
Improved Data Sharing Across Multiple Platforms
Interoperability between Snowflake and Iceberg makes it easy to share data across different platforms. This allows teams to access and analyze data without replicating it across systems, leading to improved collaboration and faster decision-making.
-
Optimizing Data Governance and Compliance
By using Snowflake Open Catalog to track metadata for Iceberg tables, organizations can ensure compliance with data governance and regulatory requirements. Centralized metadata helps maintain consistency and transparency across data systems.
-
Enhancing Performance in Data Lakes and Warehouses
Combining Snowflake’s powerful query engine with Iceberg’s optimized data storage ensures high data lake and warehouse performance. This allows businesses to handle large-scale data operations easily, improving overall efficiency.
Technical Insights and Architecture
-
Integration Architecture for Snowflake and Iceberg
The integration between Snowflake and Iceberg relies on cloud storage systems like Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage. Snowflake queries data stored in Iceberg tables via external tables, and metadata is managed through Snowflake Open Catalog. This architecture ensures that users can access and analyze data stored in Iceberg without moving or transforming it.

Fig 3: Integration Architecture for Snowflake and Iceberg
-
Data Flow and Processing Mechanisms
Data flows between Snowflake and Iceberg, allowing users to query Iceberg tables directly within Snowflake. Snowflake’s compute engine processes queries, while Iceberg manages data storage and metadata. This separation of concerns allows for optimal performance and scalability.
-
Best Practices for Seamless Interoperability
To ensure seamless interoperability, follow best practices such as:
-
Partition data effectively in Iceberg tables to optimize query performance.
-
Refresh external volumes regularly to ensure Snowflake has access to the most up-to-date data.
-
Implement proper access controls to ensure data security and compliance.
Future of Data Interoperability
-
Innovations in Data Catalogs and Table Formats
As data architectures evolve, new features and capabilities will emerge in data catalogs and table formats. Snowflake and Iceberg will continue to innovate, providing even more powerful tools for managing and analyzing data. -
The Role of Cloud-Native Technologies
Cloud-native technologies will continue to play a critical role in driving data interoperability. Platforms like Snowflake and Iceberg are designed to scale with the cloud, enabling businesses to efficiently manage vast amounts of data. -
Predictions for Snowflake and Iceberg Ecosystem
The future of the Snowflake and Iceberg ecosystem is bright, with ongoing developments in data management, querying capabilities, and interoperability. Expect further integration and performance optimization advancements, making data management even more seamless.
Integrating Snowflake and Apache Iceberg allows organizations to leverage the best of both worlds—high-performance querying and scalable, efficient data storage. This interoperability enhances data management, collaboration, and analytics across platforms, empowering businesses to unlock the full potential of their data. By adopting Snowflake and Iceberg, organizations can ensure that their data architecture is robust and future-proof.
.webp?width=1921&height=622&name=usecase-banner%20(1).webp)




