Large Language Model in Manufacturing Industries
Manufacturing industries have been rapidly evolving, embracing technological advancements to enhance operations, improve efficiency, and maintain competitiveness. Large language models (LLMs) have gained traction in manufacturing processes. This blog will explore how LLMs are utilized in manufacturing industries. Additionally, we will discuss potential Ethical Considerations of Using Large Language Models and the future of Large Language Models in Manufacturing Industries.
Advantages of LLMs in Manufacturing Industries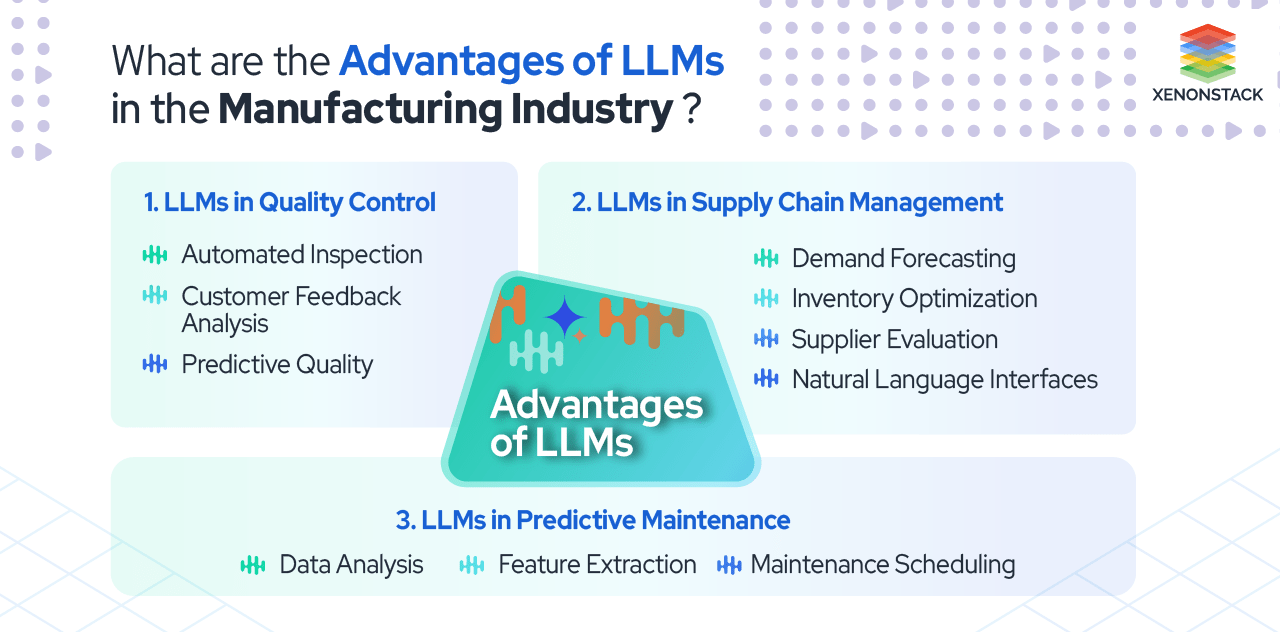
1. LLMs in Quality Control
Automated Inspection
-
Recognize patterns and anomalies in product specifications, enabling automated inspections.
-
Identify deviations from quality standards and flag products for closer inspection or rejection.
Customer Feedback Analysis
-
Analyze customer reviews and feedback, extracting insights about product performance and recurring issues.
-
Manufacturers can use this information for improvements.
Predictive Quality
-
Analyze historical and real-time sensor data to predict potential quality issues before they occur.
-
This enables proactive quality control measures.
2. LLMs in Supply Chain Management
Demand Forecasting
-
Analyze historical sales data, market trends, and external factors to generate accurate demand forecasts.
-
This helps optimize inventory levels and production schedules.
Inventory Optimization
-
Analyze data on inventory turnover rates and supplier performance, optimizing inventory levels, reducing costs, and minimizing stockouts.
Supplier Evaluation
-
Assess supplier performance by analyzing data on delivery times, quality, and pricing.
-
Informed decisions about supplier relationships are made.
Natural Language Interfaces
-
Provide natural language interfaces for supply chain management systems, enhancing user interaction with data and systems, resulting in faster decision-making.
3. LLMs in Predictive Maintenance
Data Analysis
-
Analyze data from sensors, maintenance logs, and historical records to identify patterns indicating potential equipment failures.
-
This enables preemptive maintenance.
Feature Extraction
-
Identify and extract relevant features from data, such as abnormal vibrations or temperature fluctuations, indicating potential equipment failures.
-
Predictive insights enable maintenance teams to schedule activities for equipment at high risk of failure during optimal time windows, minimizing production disruptions.
Ethical implications associated with the utilization of extensive language models
1. Biases in Training Data:
-
Data Bias: The training data may contain biases related to race, gender, or socioeconomic factors that LLMs could perpetuate when making decisions or providing recommendations.
-
Impact on Decision-Making: If carefully managed, LLMs could avoid inadvertently making biased decisions in hiring, supplier selection, or product quality assessment, leading to discriminatory outcomes.
-
Mitigation Strategies: Companies must employ rigorous data preprocessing techniques and constantly monitor LLM outputs to identify and address potential biases.
2. Privacy and Security Concerns:
-
Data Privacy: LLMs require access to extensive datasets, some of which may contain sensitive customer, team member, or intellectual property information. Ensuring data privacy and compliance with regulations like GDPR is paramount.
-
Cybersecurity: Manufacturing environments are increasingly connected, and LLMs may become cyberattack targets. Safeguarding the models against data breaches and malicious use is crucial.
-
Transparency: Maintaining transparency in how data is collected, used, and protected is essential to build trust among stakeholders.
3. Ethical and Transparent Usage:
-
Clear Guidelines: Developing explicit guidelines and policies for the ethical utilization of LLMs is crucial, ensuring that employees comprehend the limitations and expectations surrounding their application.
-
Accountability: Hold individuals and teams accountable for the ethical implications of LLM-driven decisions, including regular audits and assessments of model behavior.
-
Transparency: Be transparent with customers, employees, and other stakeholders about using LLMs, particularly when making critical decisions that affect them.
-
Continual Evaluation: Evaluate the ethical implications of LLM usage and adapt policies as necessary to address emerging challenges.
The Future of Large Language Models in Manufacturing Industries
The potential future developments and applications of LLMs in manufacturing focusing on how they could enhance worker safety, reduce waste, increase sustainability, impact the job market, and necessitate workforce retraining and reskilling.
1. Enhancing Worker Safety with LLMs
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
|
Real-Time Safety Alerts |
LLMs analyze sensor data and historical safety records to predict potential workplace hazards in real-time. Workers receive instant alerts, preventing accidents before they occur. |
|
Virtual Training and Simulations |
LLMs facilitate immersive virtual training programs, allowing workers to practice safety protocols and emergency responses in realistic simulations. |
|
Enhanced Ergonomics |
LLMs may assist in designing ergonomic workspaces and equipment, reducing workplace injuries and improving overall worker well-being. |
2. Reducing Waste and Increasing Sustainability with LLMs
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
|
Optimized Resource Management |
LLMs predict equipment maintenance needs, reducing unplanned downtime and minimizing resource waste. |
|
Energy Efficiency |
By analyzing energy consumption data, LLMs optimize energy usage in manufacturing processes, reducing costs and environmental impact. |
|
Waste Reduction |
LLMs optimize material usage, leading to reduced waste and promoting more sustainable manufacturing practices. |
3. Impact on the Job Market and Workforce
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
|
Shift in Job Roles |
The integration of LLMs may lead to a shift in job roles, with a greater focus on data analysis, LLM management, and human-AI collaboration. |
|
Retraining and Reskilling |
Companies must invest in retraining and reskilling programs to equip the workforce with the skills required to operate alongside LLMs. |
|
Job Creation |
While some jobs may evolve or be replaced, using LLMs can create new job opportunities in AI development, data analysis, and implementation. |
4. Predictive Analytics and Quality Control
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
|
Advanced Predictive Maintenance |
Future LLMs will offer more accurate predictive maintenance capabilities, reducing equipment downtime and maintenance costs. |
|
Quality Control Enhancement |
LLMs will continue to improve quality control by identifying defects and deviations from specifications more efficiently, resulting in higher product quality. |
5. Customization and Personalization
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
|
Product Customization |
LLMs will enable the efficient customization of products to meet individual customer preferences, leading to increased customer satisfaction and brand loyalty. |
|
Personalized Customer Support |
LLMs Chatbots and virtual assistants will provide extremely personalized customer support, thereby improving the overall customer experience. |
6. Supply Chain Optimization
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
|
Autonomous Supply Chains |
LLMs will play a central role in independent supply chains, optimizing inventory management, demand forecasting, and logistics. |
|
Global Supply Chain Transparency |
LLMs will provide real-time insights into global supply chain operations, enabling faster responses to disruptions and ensuring transparency. |
Conclusion
The future of Large Language Models in manufacturing industries holds immense potential for innovation, safety enhancement, sustainability, and efficiency. While integrating LLMs will likely reshape the job market, it also offers opportunities for workforce development and the creation of new roles. Manufacturers that embrace these advancements and prioritize workforce readiness will be well-positioned to thrive in this evolving landscape, reaping the benefits of LLM-driven transformations.
-
What is the importance of Generative AI in manufacturing industry?
-
Future Scope of Large Language Models in the world
.webp?width=1921&height=622&name=usecase-banner%20(1).webp)