What is Laravel Dockerfile?
Running Containers at any real-world scale requires container orchestration, and scheduling platform like Docker Swarm, Apache Mesos, AWS ECS but the most popular out of it is Kubernetes. Kubernetes is an open source system for automating deployment and management of containerized applications. In this post, We’ll share the process how you can Develop and Deploy Microservices based PHP Laravel Application on the Container Environment - Docker and Kubernetes and adopt DevOps in existing PHP Applications.A set of operating principles, and a collection of practices that enable application development teams to deliver changes more reliably and regularly. Click to explore about, Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery
Deploying Laravel Dockerfile in Kubernetes
To follow this guide you need -- Kubernetes
- Kubectl
- PHP Laravel Application Source Code
- Dockerfile
- Container-Registry
Kubernetes Automation
It is an open source platform that automates container operations, and Minikube is best for testing Kubernetes.Setting Up Kubectl
Kubectl is command line interface to manage Kubernetes cluster either remotely or locally. To configure kubectl on your machine follow this link.Shared Persistent Storage
Shared Persistent Storage is permanent storage that we can attach to the Kubernetes container so that we don`t lose our data even when container dies. We will be using GlusterFS as the persistent data store for Kubernetes container applications.PHP Application Source Code
Application Source Code is source code that we want to run inside a Kubernetes container.Using DockerFile
Dockerfile contains a bunch of commands to build PHP Laravel application.Container Registry
The Registry is an online image store for container images. Below mentioned options are few most popular registries.
- Private Docker Hub
- AWS ECR
- Docker Store
- Google Container Registry
A Docker registry stores and distributes Docker images, further enabling you to complete operate and optimize image management workflow. From the Article, Docker Container Overview
Writing a Dockerfile for Laravel
The below-mentioned code is sample Dockerfile for PHP Laravel applications. In which we are using Apache Maven 3 as the builder for PHP Laravel applications and OpenJDK 8 as a base development environment. Alpine Linux is used due to its very compact size. Below mentioned is the sample Apache2 config file for Laravel application. Create a file name laravel . conf and add the below-mentioned code to it.Building Laravel Docker Image
The below-mentioned command will build your application container image.Publishing Laravel Docker Container Image
Now we publish our PHP Laravel application container image to any container registry like Docker Hub, AWS ECR, Google Container Registry, Private Docker Registry. Today I will be using Azure container registry for publishing container images. You also need to Sign UP to Azure Cloud Platform then create container registry by using the link. Now use this link to Pull and Push to Azure Container registry. Similarly, we can push or pull any container image to any of the below-mentioned container registries like Docker Hub, AWS ECR, Google Container Registry, Private Docker Registry etc.Publishing Java Container Image
This process will enable Publishing Java application container images to any container registry using docker hub registry and Kubernetes cluster. Create a account on docker hub and create a Public/Private Repository of your application name. To login to your docker hub account. Execute the below-mentioned command.$ docker login
$ docker tag < name of your application > : < version of your application > < your docker hub account > /:
$ docker push < your docker account > /:
Setting Persistent Volume
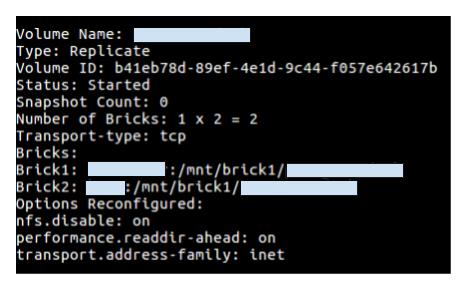
Persistent Volume is only required if your application has to save some data other than a database like documents, images, video etc then we need to use the persistent volume that kubernetes support like was AWS EBC, CephFS, GlusterFS, Azure Disk, NFS etc. I will be attaching GlusterFS volume as a persistent volume to the kubernetes container. GlusterFS volumes are very simple and easy to create. Follow the below mentioned commands.$ gluster volume create < application name > replica 2 transport tcp < node 1 > : /mnt/brick
1 / < application name > < node 2 > : /mnt/brick
1 / < application name >
$ gluster volume start < application name >
$ gluster volume info < application name >
Creating Deployment files for Kubernetes
Deploying application on kubernetes with ease using deployment and service files either in JSON or YAML format.- Deployment File
apiVersion: extensions / v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: < name of application >
namespace: < namespace of Kubernetes >
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s - app: < name of application >
spec:
containers:
-name: < name of application >
image: < image name > : < version tag >
imagePullPolicy: "IfNotPresent"
ports:
-containerPort: 7102
volumeMounts:
-mountPath: /data
name: < name of application >
volumes:
-name: < name of application >
glusterfs:
endpoints: glusterfs - cluster
path: < name of application >
readOnly: false
- Service File
apiVersion: v1https://www.xenonstack.com/use-cases/stream-analytics-iot/
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
k8s - app: < name of application >
name: < name of application >
namespace: < namespace of Kubernetes >
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
-port: 7102
selector:
k8s - app: < name of application >
- Deployment File
- Service File
Running Laravel Dockerfile in Kubernetes
PHP Laravel Container can be deployed either by Kubernetes Dashboard or Kubectl (Command line). I`m explaining command line that you can use in production Kubernetes cluster. Now we have successfully deployed PHP Laravel Application on Kubernetes.Verifying Application Deployment
We can verify application deployment either by using Kubectl or Kubernetes Dashboard. Below mentioned command will show you running pods of your application with status running/terminated/stop/created. Result of above command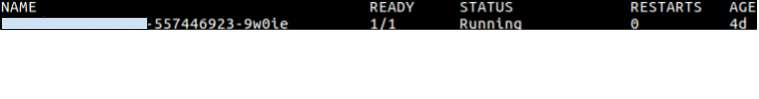
Testing Application Deployment
Get the External Node Port using the below-mentioned command. External Node Port is in the range from 30000 to 65000.Laravel Docker Container Scaling
Your PHP Laravel application should be the stateless application before you do application scaling in kubernetes. You can scale out an application in so many ways. Here I have mentioned two of them which are mostly used.- Using Kubectl
- Using Kubernetes Dashboard
Troubleshooting Laravel Docker Container
- Check Status of Pods.
- Check Logs of Pods/Containers.
- Check Service Port Status.
- Check requirements/dependencies of application.
How Can XenonStack Help You?
- Get in Touch with us for Container Security Solutions and Strategy
- Learn more about the Best Practices Securing Docker Container
.webp?width=1921&height=622&name=usecase-banner%20(1).webp)


