Role of Metadata in Agentic Systems
Metadata serves not merely as a supplementary component but as the essential foundation that enables AI agents to function effectively within enterprise environments. Metadata's role has evolved from basic data description to becoming the crucial infrastructure that powers sophisticated AI agents.
Metadata as the Cognitive Foundation for AI Agents
First, metadata serves as the cognitive foundation for AI agents, enabling four critical capabilities: reasoning support, external memory enhancement, execution capabilities, and planning functions.
Integrating descriptive, structural, administrative, and semantic metadata can help agents understand context, maintain knowledge structures, and make informed decisions.
This multi-layered approach to metadata management creates a comprehensive framework that supports increasingly sophisticated AI operations.
In Practice: Solutions like ElixirData's Agents leverage semantic metadata to enhance agent reasoning by establishing relationships between data assets, enabling agents to understand not just what data exists, but its business meaning and relationships.
Metadata Management with LLM Mesh Architecture
Second, the convergence of metadata management with LLM Mesh Architecture demonstrates how metadata facilitates the creation of distributed, specialized AI agents while maintaining system coherence. Metadata enables agent communication, task orchestration, and knowledge sharing across distributed systems.
This is particularly evident in how semantic metadata creates bridges between different domain-specific agents and their respective knowledge bases.
Metadata in Enterprise Governance and Compliance
Third, metadata's role in enterprise settings extends beyond technical implementation to encompass governance, compliance, and scalability considerations. Organizations must view metadata management as a strategic imperative, particularly as AI agents become more autonomous. Administrative metadata ensures appropriate access controls and audit capabilities, while semantic metadata enables agents to operate within defined business constraints.
The depth of metadata's importance becomes apparent when examining how it enables advanced agent capabilities.
Metadata creates a semantic layer that allows agents to understand not just the structure of data but its meaning and relationships. This semantic understanding is crucial for agents to make context-aware decisions and adapt to new situations. Furthermore, integrating different metadata types creates a comprehensive framework that supports operational efficiency and governance requirements.
The evolution of software architectures towards distributed agentic systems places increasing demands on metadata management. As systems become more distributed and autonomous, metadata must evolve to support more sophisticated interaction patterns and knowledge structures. This evolution is evident in the emergence of hybrid approaches that combine traditional metadata management with AI-powered capabilities.
Metadata serves as a bridge between traditional enterprise systems and emerging AI capabilities, particularly in how it enables the creation of sophisticated knowledge graphs and ontologies that power AI agent decision-making. Metadata is essentially "data about data." It provides descriptive, structural, and contextual information, making other data easier to understand, locate, and use effectively. By capturing essential details—such as a dataset's origin, structure, purpose, relationships, and meaning—metadata enables data to be organized and contextualized.
Currently, much of the focus in AI is on high-profile generative models, representing only the visible tip of the AI Iceberg. However, beneath the surface lies the foundation: data. What sits below determines what can happen above, so organizations must first organize their data by prioritizing metadata.
Metadata can be divided into four main types:
🔵 Descriptive Metadata: This includes information that helps identify and locate data. For example, a book’s metadata might contain the title, author, publication date, and genre. In a digital setting, descriptive metadata could include tags, keywords, or descriptions, making data easier to search and retrieve.
🔵 Structural Metadata: This describes how data is organized or formatted. For instance, a database might define table relationships or document structures, helping to ensure data is correctly interpreted, stored, and processed.
🔵 Administrative Metadata: This encompasses information needed to manage data, such as data ownership, access permissions, or retention policies. Administrative metadata is crucial for data governance, ensuring data is properly maintained and protected.
🔵 Semantic Metadata connects data to meaning, especially in the context of AI and knowledge management. Using ontologies and knowledge graphs, semantic metadata establishes relationships and contexts, helping AI "understand" distinctions in data—such as the difference between a "financial asset" and a "physical asset."
Semantic metadata gives data meaning. By adding semantics to the metadata itself, we make all metadata meaningful.
While this might sound complex, it’s quite achievable in practice. By using ontologies and knowledge graphs, you can unify Descriptive, Structural, and Administrative metadata within a semantic framework. This creates a single Semantic Layer over all your organisation's data.
AI can assist in building this Semantic Layer over your data, leveraging the general semantics of natural language. It can then use that Semantic Layer to interface more seamlessly with the specific semantics of your organization's data when answering questions at runtime.
The concept is simple, but implementing it requires time and effort—and time is running out. Organizations need to redirect resources from prototype AI projects and vanity showcases to the real task at hand: preparing their data to be effectively utilized by AI.
Metadata is essential information that helps us understand and use information assets throughout their life cycles. Taken From Article, Enterprise metadata management (EMM)
What is Metadata?
Correct metadata definition is the first step in managing metadata.
Although others prefer to refer to metadata as "data about data," that is simply one aspect of the situation.
We also refer to Metadata as "what identifies data."
Yet another incomplete definition. In actuality, metadata encompasses much more than just a data description.
Metadata plays more and more responsibilities as data complexity rises.
Metadata sometimes relates to quarterly revenues from a business perspective. Other times, it might talk about the data warehouse's source-to-target mappings.
What is Metadata Management?
Metadata management is the most crucial process for a successful digital initiative plan. It is currently essential for managing an organization's information assets due to the advent of distributed architectures like Big Data and Cloud that may result in siloed systems and data.
Metadata management can be defined as an orchestration layer of processes, policies, and technologies for cataloging information/data assets within the enterprises
Metadata management is the practice of cleaning, classifying, and organizing data to ensure its accuracy, integrity, consistency, and usability.
Metadata management is the foundation for data discovery, search, collaboration, quality, and governance. It uses a Layered Approach for data analysis, labeling, and classification. With more control over their data, companies (and their business users) can discover it quickly and use it for various operations.
Challenges without Metadata Management
Businesses and IT departments need high-quality metadata that keeps their data landscape tidy and structured. A company can only realize the value of its data with properly maintained metadata. The organizations that refuse to acknowledge the significance of it cannot answer the following:
-
What reports already exist? Do we need to spend money and make everything from scratch again?
-
Where did the data originate from, and what does it stand for?
-
How do systems transport data around?
-
Who exactly has access to the information?
-
Which data-related activities are governed by which regulations?
A few effects of poor metadata management include the inability to coordinate sales, marketing, finance, and business intelligence and governance.
Why Metadata Management Required?
Because of the following, organizations must include it in their data management practices:
-
Improved Consistency: Establishes a uniform definition of Metadata throughout the business to prevent problems with data retrieval due to conflicting terminologies.
-
Better Data Quality: Metadata management solutions usually use automation to spot problems and inconsistencies with data in real-time.
-
Faster Access to Insights: Data teams can complete projects more quickly, and data scientists have more time to study data and derive real business value.
-
Cost Savings: The efficiency improvements and repeatable procedures used in metadata management cut down on redundant spending and extra expenses like storage fees.
How can Metadata management help the business?
A metadata management framework consists of tools for capturing, integrating, managing, and publishing metadata. It includes a repository for storage, an access portal for retrieval, discovery and mapping tools for exploration, collaboration features for teamwork, and analytical capabilities for insights.
Components of a Metadata Management Framework
-
Metadata Strategy: A high-level plan that aligns with the organization's data management strategy and supports business goals.
-
Metadata Architecture: Defines the model, standards, and guidelines for consistent Metadata across the organization.
-
Metadata Governance: Establishes policies, procedures, and controls for accurate, secure, and compliant metadata management.
-
Metadata Tools and Technologies: Enables effective metadata management through tools like data modeling, repositories, profiling, and lineage.
-
Metadata Processes and Workflows: Defines processes for capturing, storing, and maintaining metadata, ensuring timely updates and proper documentation.
-
Metadata Integration: Integrates metadata from diverse systems to comprehensively view data assets.
-
Metadata Usage and Analytics: Leverages metadata for data analytics, discovery, and governance support.
Benefits of Using a Metadata Management Framework
The key benefits of a metadata management framework include:
-
Enhanced Search and Accessibility: The framework provides a unified portal with role-based views and advanced search capabilities. This enables efficient data location and access.
-
Comprehensive business semantics management: The framework supports managing business glossaries, synonyms, terms, and relationships. It also facilitates rule definition, custom data types, and taxonomies to understand the business context comprehensively.
-
Interoperability: The metadata management framework promotes shared understanding through standard vocabularies, facilitating seamless data utilization across applications and workflows.
-
Usage Tracking: The framework offers visibility into data consumption and access logs, allowing organizations to monitor and analyze data usage for informed decision-making.
What are the best practices for managing metadata?
In today's data-flooded world, it is a complex task. While many businesses now understand its significance, they still need help knowing where to begin. We've listed a few options for you to think about: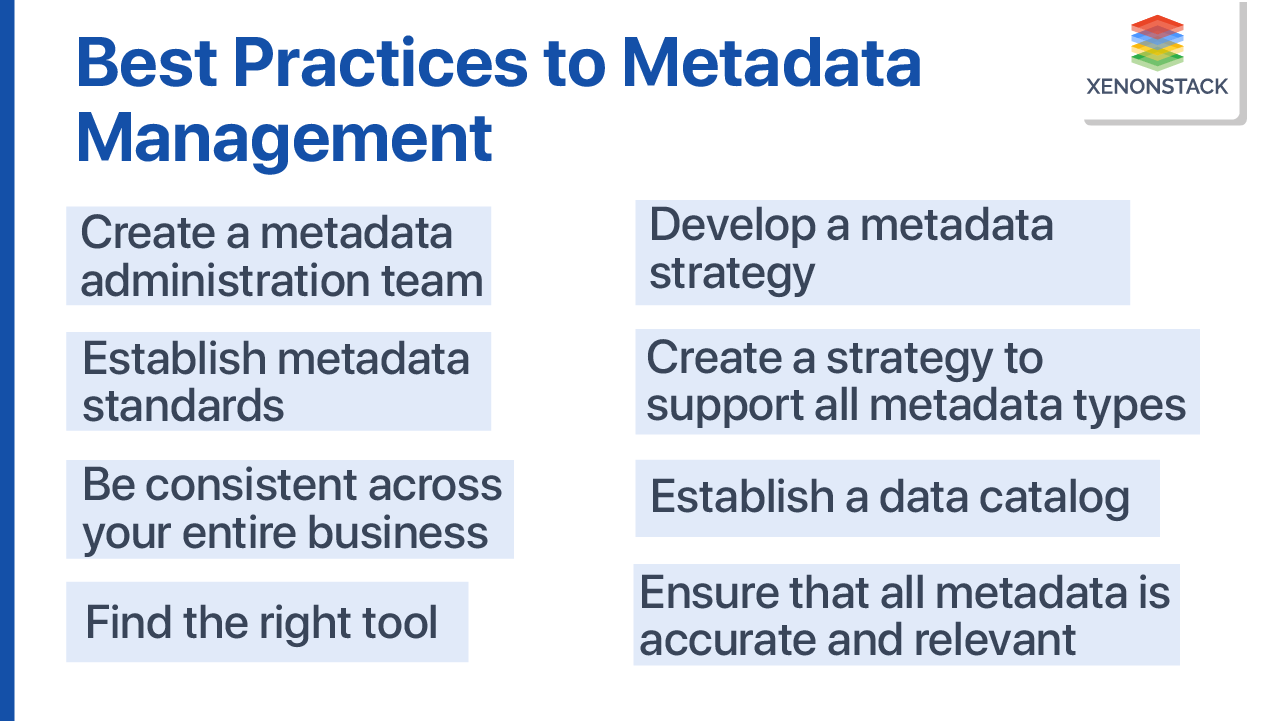
Create a Metadata Administration Team
If the organization doesn't have a metadata administration team, the initial objective should be to create one. Then, hire qualified, experienced professionals with expertise in data management to guide and manage the metadata processes.
Develop a Metadata Strategy
The basis of successful metadata management is to design a strategy that supports business goals. We should also be able to share that strategy with the key stakeholders. It should answer the following queries:
The data asset is about what?
-
Descriptions (tables, columns)
-
Keywords or tags
-
Themes or categories
Why does the data asset exist?
-
Data source
-
Lineage
-
Impact analysis
The data asset is from where?
-
Spatial coverage
-
Language
-
Business domains
Who is responsible for the data asset?
-
Creator or owner
-
Contributors or experts
-
Point of contact
When was the data asset created and updated?
-
Creation date
-
Last updated or modified date
-
Update frequency
How can the data asset be used?
-
License
-
Classification
-
Use cases
Empower the entire stack with a new way to store and analyze data solutions that are secure, agile, flexible and cost-effective than traditional data management systems. Taken From Article, Enterprise Data Lake Services and Solutions
Establish Metadata Standards for your Company
Standards for metadata are rules, directives, or formats to be followed to organize and store metadata. The metadata standardization will act as a basis for the metadata management process.
Popular metadata standards, like the ISO 158369 standard and the Dublin Core Metadata Element Set, define fundamental characteristics for representing metadata resources.
Ensure that all Metadata is Accurate and Relevant
Organizations should ensure that the available metadata list is correct and relevant.
Create templates for each type of content or document, or use pre-populated metadata from a database, spreadsheet, or another frequently used source.
Create a Strategy to Support all Metadata Types
All types of metadata, including technical, operational, and corporate, must be collected, analyzed, and processed by an organization. Therefore, the strategy should allow for the establishment of processes to utilize all types of metadata. Otherwise, the organizations could skip crucial data, leading to faulty or irrelevant business insights.
Find the Right Tool
It is challenging to manage large volumes of metadata manually. So, assess your requirements and pick the tool that best suits your workflow. Ensure integrability and scaling. Utilize AI/ML-based solutions that support active metadata management and provide vast features, such as predictive analytics.
Maintain Consistency Across the Entire Business
As soon as you've begun, add metadata consistently per your policy and chosen standards. As a result, you'll have comprehensive metadata for all of your assets. Please ensure all data users and stakeholders understand the value of metadata and pledge their support.
Establish a Data Catalog (With the Appropriate Components)
Effective metadata management depends on data catalogs. Choose and implement a data catalog with the following features:
-
Flexible search
-
The ability to gather metadata from various sources, such as object storage, on-premises systems, etc.
-
Automation of metadata collection and discovery
-
Editing and integration capabilities for business glossaries
What are the Best Tools for Metadata Management?
The best tools are highlighted below:
-
ASG Enterprise Data Intelligence
-
IBM InfoSphere Information Server
-
Collibra Platform
Types and Features of Metadata Management Tools
There are several types of metadata management tools available, including:
-
Metadata Repositories: These databases store metadata about an organization's data assets, making it easier to search, discover, and analyze data. Examples include IBM InfoSphere, Collibra, and Informatica Metadata Manager.
-
Data Modelling Tools: These tools create and manage data models, helping organizations understand data structure and relationships for easier management. Examples include ER/Studio, Embarcadero, and PowerDesigner.
-
Data Lineage Tools: These tools track data origin and flow, providing a complete view of the data's journey and supporting compliance. Examples include Informatica Metadata Manager, Manta, and Collibra.
-
Data Catalogs: These tools provide searchable inventories of data assets, including quality, lineage, and business context. Examples include Alation, Collibra, and Informatica.
-
Data Quality Tools: These tools assess and improve data quality, identifying and addressing issues. Examples include Informatica Data Quality, Talend Data Quality, and Trillium Software.
-
Data Integration Tools: These tools integrate data from different sources and systems for better management and analysis. Examples include Informatica PowerCenter, Talend Integration Cloud, and IBM InfoSphere DataStage.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Metadata Management Tool
The following are the points to consider while choosing any Metadata management tool:
Data Governance and Metadata Management
Data governance and metadata management enhance data asset management and facilitate data-driven decision-making. Here's the relationship between them:
-
Metadata is vital for data governance: Metadata offers context and comprehension to ensure data accuracy, consistency, and security. It aids in understanding data meaning, usage, lineage, and quality.
-
Metadata ensures compliance: Effective metadata management supports regulatory and compliance obligations. It helps demonstrate data accuracy, lineage, usage, security, and privacy.
-
Metadata enhances data management: Metadata simplifies management and maintenance by providing a comprehensive view of data assets. It enables data search, discovery, analysis, and identification of quality issues and supports integration and migration projects.
Metadata Standards and Policies
Metadata schemas are sets of metadata elements organized for specific purposes, such as for a particular domain or type of information resource. These schemas define the names and semantics of each element, specifying their meanings within the context of the Metadata. Optional specifications may include content rules, which dictate how the content should be formulated, representation rules (e.g., capitalization rules), and allowed values for elements, often drawn from controlled vocabularies.
Some schemas may also prescribe the syntax in which the elements must be encoded, differentiating them from syntax-independent schemas. Many contemporary schemas use Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML) or XML to define syntax. Metadata schemas established and maintained by standard organizations, such as ISO, or dedicated initiatives like the Dublin Core Metadata Initiative, are called metadata standards.
Conclusion
Although we usually overlook metadata, it is crucial for extracting value from data and using that value to resolve real-world issues. Businesses use metadata management to meet shifting client demands.
Companies that take pleasure in being the epitome of customer orientation may orient their products, marketing messages, and customer service plans with what customers desire using it. Adopting a strategy fosters a culture of data-driven innovation, cooperation, and the production of progressively wise business decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Get quick answers about Agentic Analytics, AI agents, and how ElixirData powers autonomous enterprise intelligence.
What Role Does Metadata Play in Agentic Systems?
Metadata serves as the cognitive foundation for AI agents, enabling reasoning support, memory enhancement, execution capabilities, and planning functions. It allows agents to understand data context, maintain knowledge structures, and make informed decisions in enterprise environments.
What Are the Types of Metadata in Agentic Systems?
Descriptive metadata (identifies and locates data), Structural metadata (describes data organization), Administrative metadata (manages ownership and access), and Semantic metadata (connects data to meaning through ontologies and knowledge graphs).
How Does Metadata Management Improve AI Agent Performance?
Proper metadata management enables agents to discover relevant data faster, understand business context accurately, maintain governance compliance, and orchestrate seamlessly across distributed systems without manual intervention.
What Challenges Occur Without Effective Metadata Management?
Organizations face data silos, inability to track data lineage, inconsistent definitions, compliance violations, poor data quality, difficulty locating information, and inability to answer critical questions about data origin, ownership, and usage.
How Can Semantic Metadata Enhance Agentic AI Decision-Making?
Semantic metadata creates a unified layer that helps agents understand not just data structure but its business meaning and relationships. This enables context-aware decisions, policy-aligned operations, and adaptation to new situations without manual reconfiguration.
.webp?width=1921&height=622&name=usecase-banner%20(1).webp)


