
Deploying Applications with Kubernetes
Kubernetes is an open-source system, developed by Google, an orchestration engine for managing containerized applications over a cluster of machines. It works on container technology such as Docker and rkt. It's a vast project which consists of ~30M LOC and counting, Kubernetes also know as K8s. It's a platform to control and manage the containerized applications and services and also all other things related to that containerized application that make application consistent and available to take requestsAn open-source container orchestration engine and also an abstraction layer for managing full-stack operations of hosts and containers.Click to explore about, Types of Kubernetes Architecture
How Kubernetes Works?
The main component of K8s in the cluster made up of many physical or virtual machines and each machine serves a specialized function either as a master or as a worker(node). Node has a group of containers (pods) as a deployment which represents someone's applications; pods are the primary K8s objects. Master continuously communicates with nodes regarding when to create or delete containers and also help in re-routing the traffic based on new deployments.
Kubernetes uses a controller for dealing with the logistics of how pods desired state as specified in the file. There are various types of controller each with different work but with the same goal i.e. requested no. of Pods run to the K8s according to the user's specifications. As pods can live and die according to needs, depending on application need make an application a persistent entity, done through service. A service tells how to access different pods or K8s objects via networks.
Master Node Main components
The main components of Master Node are below:
1. etcd
etcd is a simple storage system that stores the K8s cluster data (such as no. of pods, namespace, API and service details and many other things related to the cluster) in the form of a distributed key-value pair. Only accessible through the API server, and use to enables notifications to the cluster related to configuration changes.
2. Kube-API server
The master node runs the K8s API server which is a frontend to cluster and used for controlling the cluster, and also every request related to some changes to pods, service, or other changes is deal by the API server. It is like a control plane that manages, communicate across clusters.
The goal of Kubernetes for AI is to make scalable models and deployment on production most inherently. Click to explore about our, Building Enterprise AI Platform on Kubernetes
3. Kube-control-manager
Kube-control-manager handles the clusters of Pods using a reconciliation loop to achieve the desired cluster's state by running some different controller processes in the background, a process such as the endpoints controller or replication controller responsible for ensuring that the requested number of Pods run to the K8s user's specifications. If it finds the desired state not achieved, then it will do what needs to be done to achieve the specified state. Also if any changes in a service configuration occur, it scales the pod to achieve the desired state.
4. Kube-scheduler
Workloads of a node in the cluster are tracked and handled by the Kube-scheduler. It is based on resource consumption, helps in scheduling the pods on the various nodes.
5. Cloud-control-manager
It is responsible for managing controller processes with dependencies on the underlying Cloud provider. It's an abstraction layer between the APIs and the tools of a Cloud provider.
Worker Node Main components
1. Kubelet
It runs on each node which makes sure that the containers are running and are healthy. It is responsible for managing the state of the node such as starting, stopping, and maintenance of the container by following the rules described by the control manager.
2. Kube-proxy
It is a network proxy service runs on nodes in the cluster and acts as a load balancer for services running on a node.
Some basic Kubernetes terminologies
- Cluster
- Node
- Namespace
- Deployment
- Pod
- Container
- Service
Containers are helpful to move an application for deployment in different environments quickly. Click to explore about, Container Design Patterns for Kubernetes
Optimizing Kubernetes Deployment - Best Practices
In addition to the challenges and steps involved in adopting Kubernetes, it is important to follow best practices for Kubernetes deployment to ensure smooth and efficient operations. These best practices aim to optimize resource utilization, enhance security, and improve overall performance. Let's explore some of the key best practices for Kubernetes deployment:
1. Use Small Base Images
When building container images, it is recommended to use minimal and lightweight base images. This helps reduce the image size and improves the startup time of containers.
2. One Process per Container
To ensure container isolation and scalability, it is advisable to follow the principle of one process per container. This allows for better resource management and easier troubleshooting.
3. Utilize the "record" Option and Set Relevant Labels
When performing rollbacks, it is crucial to use the "record" option to capture the history of changes made to the cluster. Additionally, setting relevant labels helps in identifying and managing different components of the application.
4. Take Advantage of Sidecars
Sidecars are additional containers running alongside the main application container. They can be used for various purposes such as proxies or watchers. However, it is important to avoid using sidecars for bootstrapping, as this can complicate the deployment process.
5. Implement Readiness and Liveness Probes
Readiness probes ensure that a container is ready to receive traffic, while liveness probes determine if a container is still running correctly. These probes help in maintaining the availability and health of the application.
6. Avoid using "latest" as a Tag
Instead of using the "latest" tag for container images, it is recommended to use a relevant version or tag. This ensures better control over image updates and helps in maintaining consistency.
7. Consider using Type
NodePort for external access: While type: LoadBalancer can be used for external access, it may have limitations depending on the environment. Using type: NodePort allows for easier management and routing of traffic to the application.
8. Utilize static IPs and Route External Services to Internal Ones
To ensure consistent communication between external and internal services, it is advisable to use static IPs and route external services to internal ones. This helps in maintaining stability and reliability.
Kubernetes Security Best Practices
To enhance the security of your Kubernetes deployment, it is important to follow best practices such as not trusting random base images, using non-root users inside containers, setting the file system to read-only, and logging everything to stdout and stderr. Additionally, implementing role-based access control (RBAC) helps in managing cluster access and permissions effectively.
1. Leverage Helm Charts
Helm is a package manager for Kubernetes that allows for easy deployment and management of applications. Using Helm charts helps in simplifying the deployment process and ensures consistency across different environments.
2. Organize Projects or Applications with Namespaces
Namespaces provide a way to logically isolate and manage different projects or applications within a Kubernetes cluster. By organizing resources into namespaces, it becomes easier to manage and monitor deployments.
3. Define Resource Requests and Limits
To optimize resource utilization and avoid resource contention, it is recommended to define resource requests and limits for containers. This helps in efficient resource allocation and prevents one container from monopolizing resources.
4. Gracefully Terminate Pods
When scaling down or terminating Pods, it is important to use the grace period option. This allows running processes within the Pods to gracefully shut down, ensuring data integrity and minimizing disruptions.By following these best practices, organizations can optimize their Kubernetes deployments, enhance security, and improve overall operational efficiency. It is important to continuously review and update these practices as new features and improvements are introduced in the Kubernetes ecosystem.
Best Implementation of Kubernetes approach for DevOps to configuration management and deployment at a large scale. Java Microservices Application on Kubernetes
What are the Best Tools for Kubernetes?
Here are some of the top Kubernetes tools that can enhance your deployment and configuration experience:
1. kubectl
This is a powerful command-line tool that allows you to interact with your Kubernetes cluster, enabling you to manage and control various aspects of your application.
2. kubeadm
With kubeadm, you can easily bootstrap a Kubernetes cluster, simplifying the installation and configuration process.
3. kubefed
This tool enables you to federate multiple Kubernetes clusters, allowing for seamless management and operation across different environments.
4. dashboard
The Kubernetes dashboard provides a user-friendly graphical interface for monitoring and managing your cluster, making it easier to visualize and control your applications.
5. helm
Helm is a popular package manager for Kubernetes, offering an efficient way to deploy and manage applications using pre-configured charts.
6. kompose
With kompose, you can easily convert your Docker Compose files into Kubernetes manifests, simplifying the migration of your applications to Kubernetes.
7. kubespray
This tool provides a collection of Ansible roles that automate the deployment and configuration of Kubernetes clusters, making it easier to set up and manage your infrastructure.
8. simple kube
If you're looking for a straightforward solution, simple kube is a bash script that allows you to quickly deploy a single-node Kubernetes cluster on a Linux server.
9. kube watch
For monitoring purposes, kube watch provides a convenient way to observe changes and events within your Kubernetes cluster, ensuring that you stay informed about the status of your applications. By leveraging these powerful tools, you can streamline your Kubernetes deployment and configuration process, enhancing your overall efficiency and productivity.
What are the benefits of Kubernetes?
The advantages of Kubernetes are numerous and contribute to the enhanced resilience and efficiency of organizations:
1. Enhanced Resilience
Kubernetes offers self-healing capabilities, automatically resolving container issues and ensuring minimal downtime. This maximizes application availability and provides a robust infrastructure.
2. Seamless Updates and Reversions
Kubernetes automates rollouts and rollbacks, allowing for easy updates and reversions without disrupting the system. This flexibility enables organizations to make changes while maintaining a smooth user experience.
3. Intelligent Resource Allocation
Kubernetes intelligently schedules containers based on available resources, optimizing resource utilization and ensuring efficient workload distribution. This maximizes infrastructure efficiency and ensures smooth application performance.
4. Effortless Load Balancing
Kubernetes simplifies load balancing by distributing network traffic across multiple containers. This prevents overloading and ensures responsive application performance for users.
5. Comprehensive Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Kubernetes provides robust resources tracking and logging capabilities, offering comprehensive visibility into the system. This enables effective monitoring and troubleshooting, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing issues.
6. Simplified DNS Management
Kubernetes simplifies DNS management, making it easy to manage and resolve domain names for various services within the cluster. This streamlines network resource management and enhances overall system efficiency.
By harnessing these advantages, Kubernetes empowers organizations to streamline operations, achieve greater efficiency, and ensure the reliability of their containerized applications.
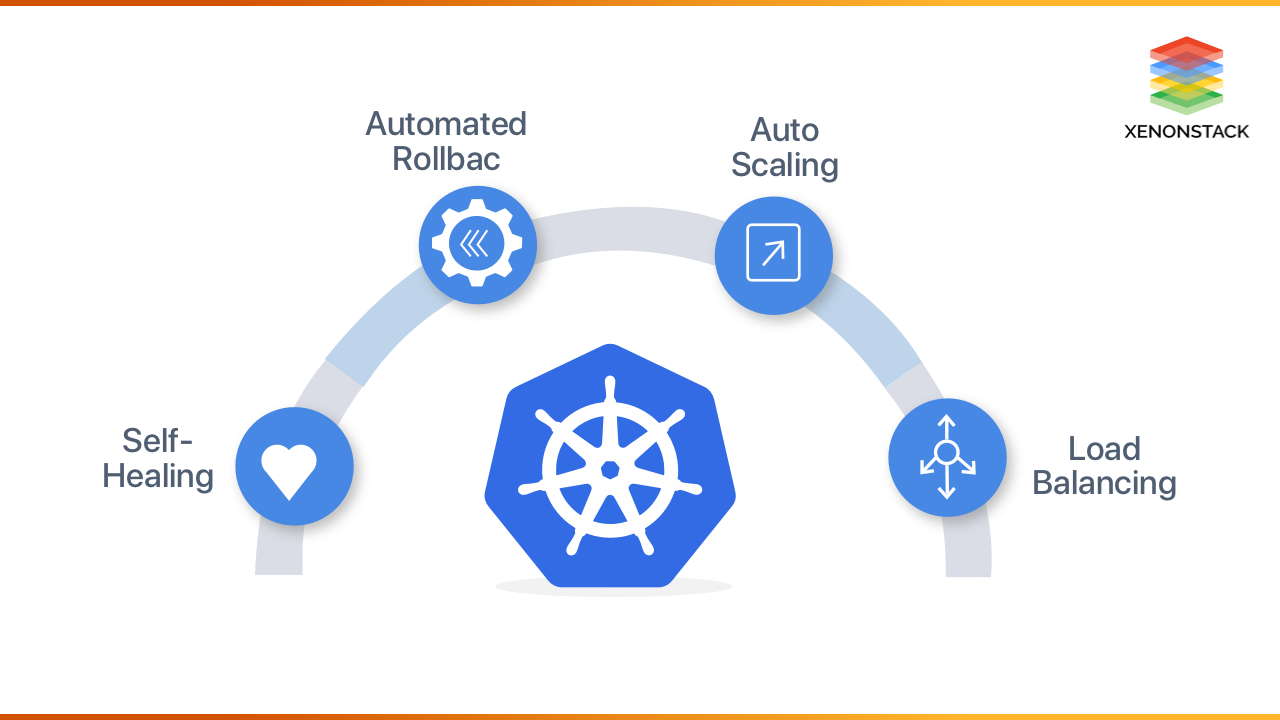
Kubernetes has solid Community supports and a large number of active contributors that helps in making Kubernetes as robust as possible and helps someones to adopt it. Kubernetes reduces the infrastructure costs in large-scale deployments, by running many containers on the same machine, resulting in the maximum use of the available resources.
Kubernetes runs both on the Cloud and On-premises, which means now K8s. It is now supported on all popular Clouds. Self-healing, that's the fundamental feature of K8s, which makes it popular. Easier Deployment, through K8s someones can deploy containers more efficiently, securely, and smoothly. It's so trendy among managing Virtual Infra, that organization is adopting it as a standard for their container deployment in production.
Kubernetes Adoption Challenges
There are lots of challenges a user can face and it all depend on the size of the organization along with their culture. Whether an organization is using on-premises cloud or a public cloud. Below are some primary challenges a user can face (based on the recent survey done by Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF).
1. Security
Security is a paramount concern when deploying applications in a Kubernetes environment. It is crucial for users to ensure that their clusters are adequately secured and protected against unauthorized access. This involves implementing role-based access control (RBAC), encrypting communication between components, and regularly updating and patching the system to address any security vulnerabilities.
2. Networking
Networking in Kubernetes involves managing communication between different components and services within the cluster. Users should configure networking policies to control traffic flow and ensure secure communication between pods. Additionally, they may need to set up load balancers or configure network plugins to facilitate communication with external services.
3. Storage
Kubernetes offers various options for persistent storage, such as volume plugins and storage classes. Users must carefully consider their storage requirements and select the appropriate storage solution for their applications. They may also need to configure access controls and manage data replication and backups to ensure data durability and availability.
4. Monitoring
Monitoring plays a crucial role in keeping track of the health and performance of a Kubernetes cluster. Users should set up monitoring tools to collect metrics and logs from various components, including nodes, pods, and containers. Tools like Prometheus and Grafana can be used to visualize and analyze the collected data, enabling users to identify and address performance issues or anomalies effectively.
5. Logging
Logging is essential for troubleshooting and debugging applications running in a Kubernetes cluster. Users need to configure logging systems to capture logs from different components and services. They can leverage tools like Elasticsearch, Fluentd, and Kibana (EFK stack) to collect, store, and analyze log data, aiding in the identification and resolution of any issues that may arise.
By addressing these challenges effectively, users can ensure the security, reliability, and performance of their Kubernetes deployments. It is important to stay updated with the latest best practices, leverage the available tools and technologies, and seek assistance from the Kubernetes community to overcome these challenges successfully.
How to adopt Kubernetes?
To adopt Kubernetes, you need to follow a series of steps that involve setting up a cluster, deploying an application, creating a Dockerfile, connecting to the cluster, and deploying a Docker image. Let's take a closer look at each step:
Step -1 - Set Up a Cluster
Setting up a cluster involves creating a master node and multiple worker nodes. The master node is responsible for managing the cluster, while the worker nodes run the containers. You can use tools like kubeadm, kops, or AKS (Azure Kubernetes Service) to set up the cluster.
Step - 2 - Deploy an Application to Kubernetes
Once the cluster is set up, you can deploy your application. Kubernetes uses YAML or JSON configuration files to define the desired state of your application. These files specify the number of replicas, container images, ports, and other configuration details. By applying these configuration files, Kubernetes ensures that the desired state is achieved.
Step - 3 - Create a Dockerfile
A Dockerfile is a text file that contains instructions for building a Docker image. It specifies the base image, copies files into the image, and defines the commands to run when the container starts. Creating a Dockerfile allows you to package your application and its dependencies into a container image that can be deployed to Kubernetes.
Step - 4 - Connect to Cluster
To interact with the Kubernetes cluster, you need to establish a connection. This can be done using the Kubernetes command-line tool, kubectl. By configuring the appropriate credentials and pointing kubectl to the cluster, you can perform various operations, such as deploying, scaling, and monitoring your application.
Step - 5 - Add Cluster and Login Docker Registry
To deploy a Docker image to Kubernetes, you need to have access to a Docker registry. A Docker registry is a repository for storing and distributing Docker images. You can use popular registries like Docker Hub or create your own private registry. Once you have access to a registry, you need to configure Kubernetes to authenticate and pull images from the registry.
Step - 6 - Deploy a Docker Image
With the cluster set up and the Docker image available in the registry, you can deploy the image to Kubernetes. This involves creating a Kubernetes deployment object that specifies the desired state of your application. The deployment object manages the lifecycle of the application, ensuring that the specified number of replicas is running and handling rollouts and rollbacks.
Step - 7 - Build and Deploy an Image
If you make changes to your application, you'll need to rebuild the Docker image and redeploy it to Kubernetes. This process involves updating the Dockerfile, rebuilding the image, pushing it to the registry, and updating the Kubernetes deployment with the new image version. By following this workflow, you can easily iterate and deploy new versions of your application.
Step - 8 - Deploy the Private Image to Kubernetes
In some cases, you may need to deploy a private Docker image that is not publicly available in a registry. To do this, you can create a Kubernetes secret that contains the credentials needed to access the private registry. By referencing this secret in your deployment configuration, Kubernetes can pull the private image and deploy it to the cluster.
Step - 9 - Automate the Process Deployment to Kubernetes
To streamline the deployment process, you can automate it using continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) tools. CI/CD pipelines allow you to automatically build, test, and deploy your application to Kubernetes whenever changes are made to the source code. By automating the deployment process, you can ensure consistent and reliable deployments.
By following these best practices and steps, you can successfully adopt Kubernetes and leverage its powerful features for managing and deploying your applications. Kubernetes provides a robust and scalable platform for running containerized workloads, and by mastering its deployment process, you can unlock its full potential.
Compressive Approach to Kubernetes Deployment
Kubernetes is an open source platform that is being used by enterprises to manage their containerized applications across a clump of machines. To implement this tool, you are advised to take below steps to have more clarity of this tool.
- Learn more about Set up Jenkins on Kubernetes Cluster
- Enquire us to Kubernetes Security Services
.webp?width=1921&height=622&name=usecase-banner%20(1).webp)



